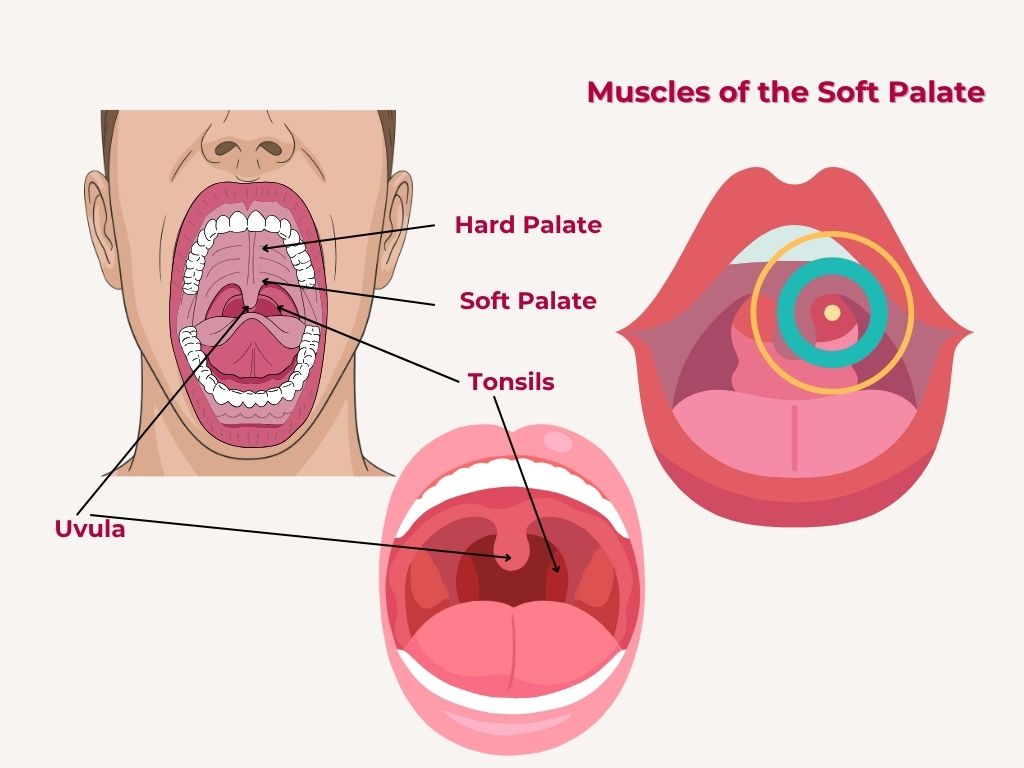
Overview
The soft palate, also known as the velum, is a muscular structure located at the back of the roof of the mouth. It plays a crucial role in speech, swallowing, and breathing.
The muscles of the soft palate are:
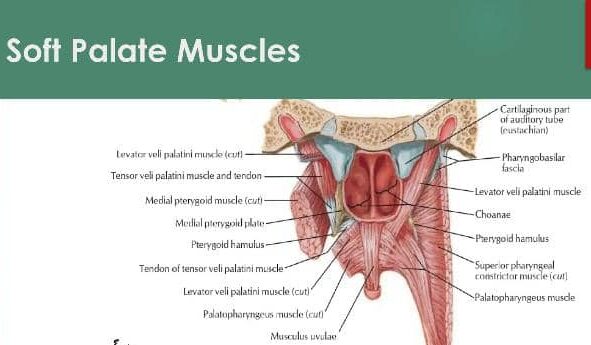
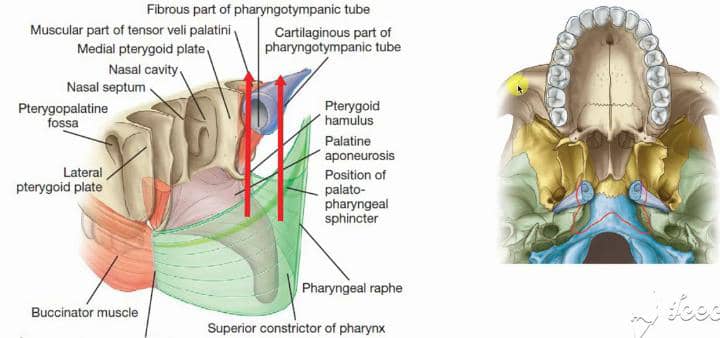
1. Tensor Veli Palatini
1. Origin: Sphenoid bone and auditory tube
2. Insertion: Palatine aponeurosis
3. Function: Tenses the soft palate and opens the auditory tube during swallowing
2. Levator Veli Palatini:
1. Origin: Temporal bone and auditory tube
2. Insertion: Palatine aponeurosis
3. Function: Elevates the soft palate during speech and swallowing
3. Musculus Uvulae
1. Origin: Palatine aponeurosis
2. Insertion: Uvula
3. Function: Shortens the uvula and helps to elevate the soft palate
4. Palatoglossus
1. Origin: Palatine aponeurosis
2. Insertion: Tongue
3. Function: Elevates the tongue and helps to constrict the oropharyngeal isthmus
5. Palatopharyngeus
1. Origin: Palatine aponeurosis
2. Insertion: Pharyngeal wall
3. Function: Elevates the pharynx and larynx during swallowing
Innervation
The muscles of the soft palate are innervated by:
-
1. Tensor veli palatini
Mandibular division of the trigeminal nerve (V3)
-
2. Levator veli palatini, musculus uvulae, palatoglossus, and palatopharyngeus
Vagus nerve (X) via the pharyngeal plexus
Functions
The muscles of the soft palate work together to:
-
1. Separate the nasal cavity from the oral cavity
During swallowing and speech
-
2. Regulate airflow
During speech and breathing
-
3. Facilitate swallowing
By elevating the soft palate and pharynx
Understanding the anatomy and function of the muscles of the soft palate is essential for diagnosing and managing disorders such as velopharyngeal insufficiency and cleft palate.
Want to Know More of
Cleft palate is a congenital anomaly that affects the roof of the mouth, occurring when the tissues that form the palate do not fuse properly during fetal development. Here’s what you need to know. . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . . .
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Nuggets of ORL-OTOLOGY
-
Nuggets of ORL-RHINOLOGY
-
Nuggets of Otorhinolaryngology-Basic sciences
-
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Soft Palate
-
Ethmoidal Arteries Ligation for Epistaxis
-
Submucous Cleft Palate (SMCP)
-
Approach to Ligation of the External Carotid Artery
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body in the nasal cavity.
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
-
Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation (ESPAL) for Epistaxis
-
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
-
Tracheostomy
-
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
-
Acute Epiglottitis And Approach To Management
-
Synoptic Overview Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
Prioritizing Support For People With Disabilities Over Unhealthy Competitions That Marginalise The Downtrodden
-
Otitic Barotrauma
-
Titbits of Informed Consent Process for a Medical or Surgical Procedure
-
Comprehensive Overview of Mpox (Monkeypox)
-
Overview Of Corrosive Ingestion - Acid & Alkalis, and Management Approach
-
Ethical Conundrum
Categories
RELATED POSTS
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.

