Overview
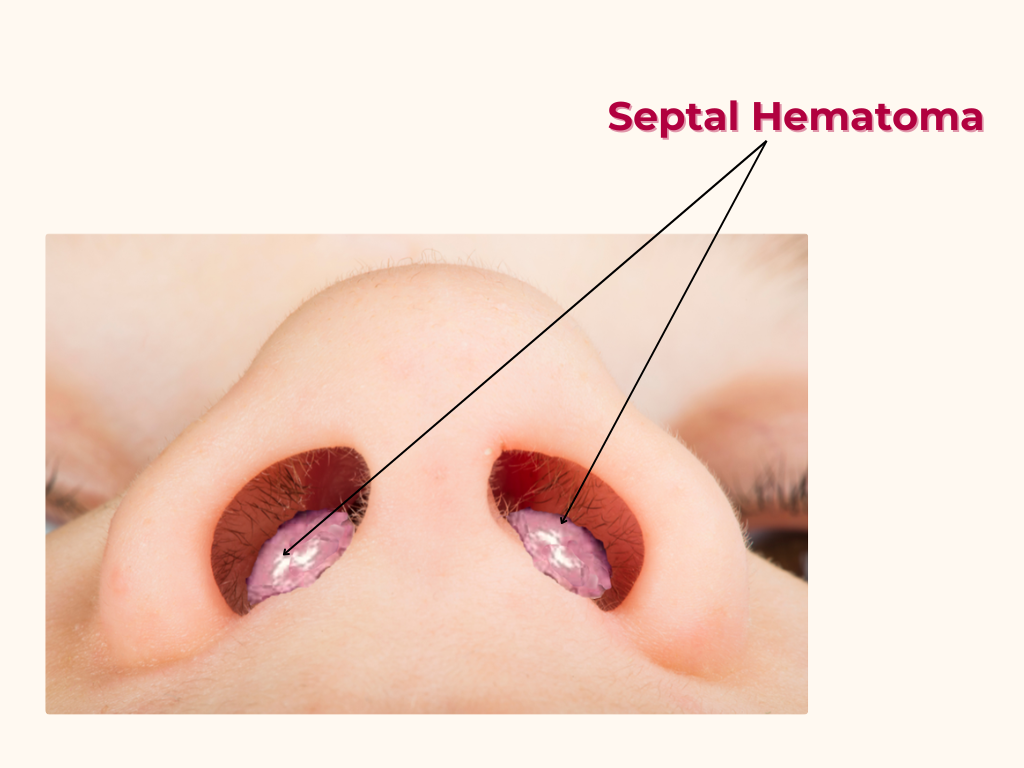
A septal hematoma is a collection of blood between the cartilage or bone of the nasal septum and its covering mucoperichondrium or mucoperiosteum.
Septal hematoma or abscess is a serious condition that requires prompt treatment to prevent complications.
Anatomy of the Nasal Septum
The nasal septum consists of:
-
1. Cartilaginous septum
The anterior part of the septum.
-
2. Bony septum
The posterior part of the septum.
-
3. Mucoperichondrium
The layer of tissue covering the cartilaginous septum.
-
4. Mucoperiosteum
The layer of tissue covering the bony septum.
Location of Hematoma or Abscess
The hematoma or abscess typically occurs between the mucoperichondrium or mucoperiosteum and the underlying cartilage or bone.
Epidemiology
Septal hematoma or abscess can occur in anyone, but it is more common in children and young adults.
Pathophysiology
The hematoma or abscess forms when blood or pus accumulates in the space between the mucoperichondrium or mucoperiosteum and the underlying cartilage or bone.
Aetiological Factors
-
1. Trauma
Nasal trauma is a common cause of septal hematoma.
-
2. Infection
Bacterial infection can lead to the formation of a septal abscess.
Symptoms and signs
Symptoms
- Nasal obstruction: Difficulty breathing through the nose.
- Nasal pain: Pain or discomfort in the nose.
- Swelling: Swelling of the nasal septum.
Signs
- Nasal septal deviation: The nasal septum may be deviated or displaced.
- Purulent discharge: Pus may be visible in the nasal cavity.
Diagnosis
Clinical Examination and Diagnosis
The diagnosis is typically made based on clinical examination and history.
Investigations
Imaging studies: CT or MRI scans may be used to assess the extent of the hematoma or abscess.
Complications
-
1. Septal perforation
Untreated septal hematoma or abscess can lead to septal perforation.
-
2. Nasal deformity
Septal hematoma or abscess can cause nasal deformity if not treated promptly.
Management
A nasal septal hematoma treatment or management can be done by the following:
-
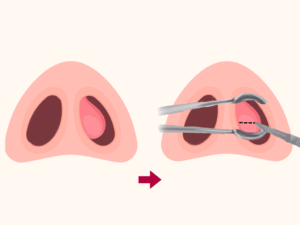
Incision and drainage:
The hematoma or abscess should be drained promptly. This procedure is done through the following steps.
Step-by-Step Technique of Incision
-
1. Preparation
The patient should be prepared for the procedure.
-
2. Anesthesia
Local anesthesia may be used to numb the area.
-
3. Incision
A small incision is made in the mucoperichondrium or mucoperiosteum, parallel to the septum.
-
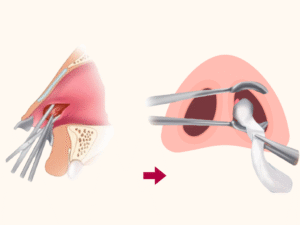
4. Drainage
The hematoma or abscess is drained, and the cavity is irrigated with saline solution.
-
5. Packing
The cavity may be packed with gauze or a nasal splint to prevent re-accumulation of blood or pus.
Post-Incision and Drainage Management
-
1. Antibiotics
Antibiotics may be prescribed to prevent or treat infection.
-
2. Nasal saline irrigations
Nasal saline irrigations may be used to keep the nasal cavity clean.
-
3. Follow-up
The patient should be followed up regularly to monitor for complications.
By following these steps, septal hematoma or abscess can be effectively managed, and complications can be prevented.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Overview of AI Tools In Modern ORL Practice
-
Nuggets of ORL-LARYNGOLOGY
-
All You Need To Know About PET Scan
-
Nuggets of ORL-PAEDIATRICS
-
Nuggets of ORL-OTOLOGY
-
Nuggets of ORL-RHINOLOGY
-
Nuggets of Otorhinolaryngology-Basic sciences
-
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Soft Palate
-
Ethmoidal Arteries Ligation for Epistaxis
-
Submucous Cleft Palate (SMCP)
-
Approach to Ligation of the External Carotid Artery
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body in the nasal cavity.
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
-
Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation (ESPAL) for Epistaxis
-
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
-
Tracheostomy
-
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
-
Acute Epiglottitis And Approach To Management
-
Synoptic Overview Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
Prioritizing Support For People With Disabilities Over Unhealthy Competitions That Marginalise The Downtrodden
-
Otitic Barotrauma
-
Titbits of Informed Consent Process for a Medical or Surgical Procedure
-
Comprehensive Overview of Mpox (Monkeypox)
-
Overview Of Corrosive Ingestion - Acid & Alkalis, and Management Approach
-
Ethical Conundrum
-
Comprehensive Overview of Laryngeal Papillomatosis and HPV Virus
-
All You Need To *Know About Gardasil*
-
Preauricular Sinus
-
Laryngomalacia - comprehensive overview
-
Flexible Laryngoscopy features of Laryngomalacia
-
Case Report of a Rare Cause of Upper Airway Obstruction In Adults
Categories
RELATED POSTS
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.