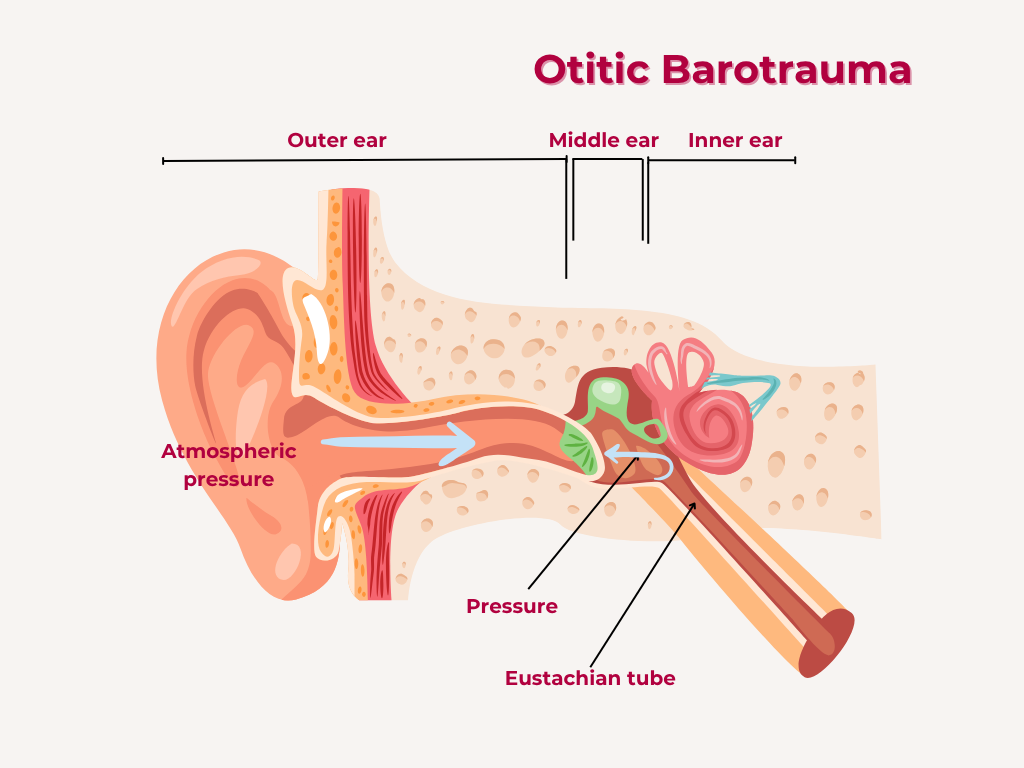
Otitic barotrauma refers to injury to the middle ear caused by changes in atmospheric pressure, often occurring during activities like flying, diving, or traveling through tunnels.
Epidemiology
-
1. Common in:
Individuals who experience rapid changes in atmospheric pressure, such as divers, pilots, and passengers on airplanes.
-
2. Prevalence:
Varies depending on the population and activity.
Pathophysiology
-
1. Pressure changes:
Rapid changes in atmospheric pressure can cause Eustachian tube dysfunction, leading to middle ear damage.
-
2. Middle ear injury:
The tympanic membrane and middle ear structures can be injured due to pressure differences. Early presentation for evaluation and management prevent complications and improves the prognostic outcome.
Symptoms and signs
Otitic barotrauma symptoms may include:
1. Ear pain: Pain or discomfort in the ear.
2. Hearing loss: Temporary or persistent hearing loss.
3. Fullness: Feeling of fullness or pressure in the ear.
4. Tinnitus: Ringing or other sounds in the ear.
Investigations
Health providers may do the following diagnosis for Otitic barotrauma:
1. Otoscopy: Examination of the ear canal and tympanic membrane.
2. Tympanometry: Assessment of middle ear function.
3. Audiometry: Hearing tests to evaluate hearing loss.
Complications
Complications include:
1. Persistent hearing loss: Long-term hearing impairment.
2. Middle ear infection: Increased risk of infection due to Eustachian tube dysfunction.
3. Tympanic membrane perforation: Rupture of the eardrum.
Management of Otitic Barotrauma
Management and Treatment for Otitic barotrauma include:
Medical Management
1. Decongestants: Medications to reduce nasal congestion and promote Eustachian tube function.
2. Analgesics: Pain relief medications.
3. Valsalva maneuver: Technique to equalize middle ear pressure.
Surgical Management
1. Myringotomy: Surgical incision in the tympanic membrane to relieve pressure.
2. Tympanostomy tubes: Insertion of tubes to ventilate the middle ear.
3. Tympanic membrane repair: Surgery to repair a perforated eardrum.
The goal of management is to alleviate symptoms, prevent complications, and restore middle ear function.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Nuggets of ORL-OTOLOGY
-
Nuggets of ORL-RHINOLOGY
-
Nuggets of Otorhinolaryngology-Basic sciences
-
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Soft Palate
-
Ethmoidal Arteries Ligation for Epistaxis
-
Submucous Cleft Palate (SMCP)
-
Approach to Ligation of the External Carotid Artery
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body in the nasal cavity.
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
-
Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation (ESPAL) for Epistaxis
-
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
Categories
RELATED POSTS
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.