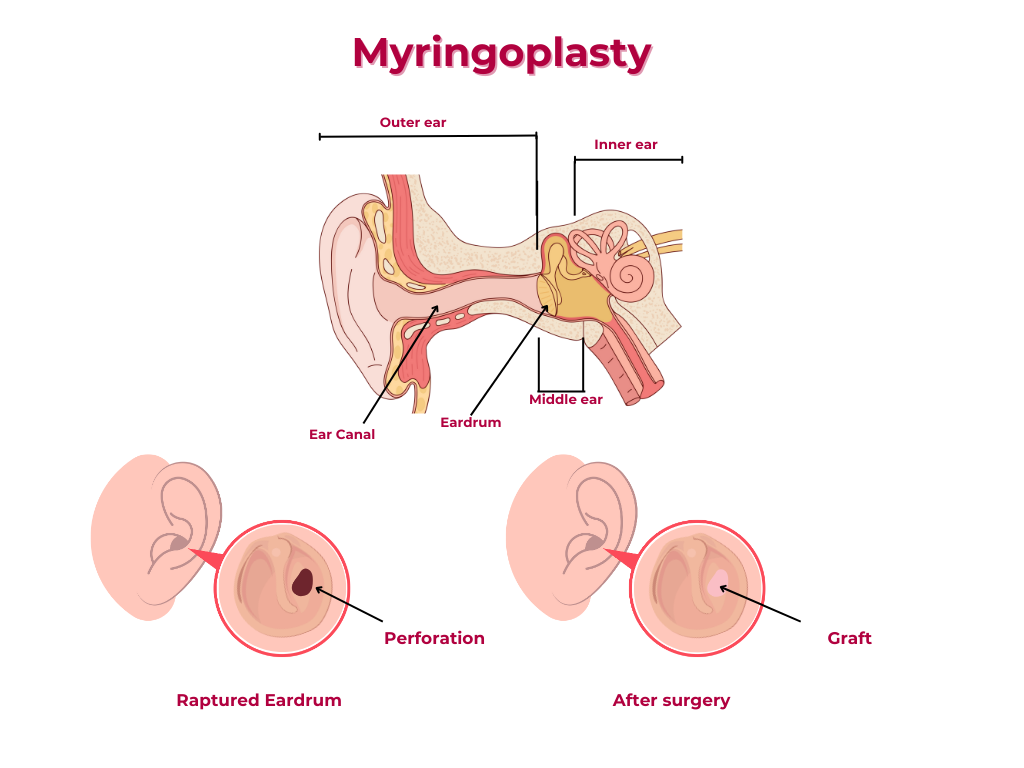
Myringoplasty is a surgical procedure perform to close a perforated tympainic membrane (ear drum).
Pre-requisites for Myringoplasty
-
1. Perforation size and location
The perforation should be relatively small (less than 50% of the tympanic membrane) and located in the central or anterior part of the eardrum.
-
2. Hearing status
The patient should have a reasonable hearing threshold, as myringoplasty is primarily aimed at improving hearing.
-
3. Middle ear status
The middle ear should be free of infection, and the ossicles (middle ear bones) should be intact.
-
4. Eustachian tube function
The Eustachian tube should be functioning properly to ensure adequate ventilation of the middle ear.
-
5. Absence of cholesteatoma
There should be no evidence of cholesteatoma, a type of skin cyst that can occur in the middle ear.
-
6. Patient's overall health
The patient should be in good overall health and free of any medical conditions that may compromise the success of the surgery.
TYPES OF MYRINGOPLASTY
Here are the types of myringoplasty, their indications, advantages, disadvantages, and success rates:
Underlay Myringoplasty
Indications
1. Small to medium-sized perforations: Perforations that are less than 50% of the tympanic membrane.
2. Anterior or central perforations: Perforations located in the anterior or central part of the tympanic membrane.
Advantages
-
1. Less traumatic
The underlay technique is less traumatic to the middle ear structures.
-
2. Faster healing
The underlay technique promotes faster healing and reduces the risk of complications.
-
3. Better hearing outcomes:
The underlay technique can provide better hearing outcomes, especially in cases with small perforations.
Disadvantages
-
1. Limited access
The underlay technique can provide limited access to the middle ear, making it more challenging to visualize and repair the perforation.
-
2. Risk of graft displacement
There is a risk of graft displacement or rejection, especially if the graft is not properly secured.
Success Rate
The success rate for underlay myringoplasty is reported to be around 80-90%.
Overlay Myringoplasty
Indications
1. Large perforations: Perforations that are greater than 50% of the tympanic membrane.
2. Posterior perforations: Perforations located in the posterior part of the tympanic membrane.
3. Recurrent perforations: Perforations that have recurred after previous repair attempts.
Advantages
-
1. Better access
The overlay technique provides better access to the middle ear, making it easier to visualize and repair the perforation.
-
2. Reduced risk of graft displacement
The overlay technique reduces the risk of graft displacement or rejection.
-
3. Improved hearing outcomes
The overlay technique can provide improved hearing outcomes, especially in cases with large perforations.
Disadvantages
-
1. More traumatic
The overlay technique is more traumatic to the middle ear structures, which can increase the risk of complications.
-
2. Slower healing
The overlay technique can result in slower healing and a higher risk of complications.
Success Rate
The success rate for overlay myringoplasty is reported to be around 70-80%.
Complications of Myringoplasty
-
1. Graft failure
The graft may fail to take, resulting in a recurrent perforation.
-
2. Infection
Infection can occur, especially if the graft is not properly secured or if the middle ear is not properly cleaned and prepared.
-
3. Hearing loss
Hearing loss can occur, especially if the middle ear structures are damaged during the procedure.
-
4. Tinnitus
Tinnitus (ringing in the ears) can occur, especially if the middle ear structures are damaged during the procedure.
-
5. Facial nerve weakness:
Facial nerve weakness or paralysis can occur, especially if the facial nerve is damaged during the procedure.
It’s essential to discuss the risks and benefits of myringoplasty with an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist to determine the best course of treatment for your specific condition.
Here’s a step-by-step outline:
Pre-Operative Steps
1. Pre-anesthetic evaluation: Assess the patient's overall health and anesthesia risks.
2. Informed consent: : Obtain consent from the patient or guardian.
3. Preparation: Prepare the operating room, instruments, and equipment.
Operative Steps
1. Positioning: Place the patient in a supine position with their head turned to the side.
2. Anesthesia: Administer general anesthesia and/or local infiltration of incision site.
3. Cleaning and preparation: Clean the ear canal and surrounding area with povidone iodine or any appropriate cleaning antiseptic.
4. Incision: Make an incision in the external auditory canal (permeatal approach) or behind the ear (postaural approach).
5. Exposure: A meatal flap is meticulously raised to the annulus for permeatal approach. Expose the tympanic membrane and surrounding structures. Edges of perforation freshened.
6. Dissection: Dissect car perforated area of the tympanic membrane.
7. Graft harvesting: Harvest a graft from the temporalis fascia, perichondrium, or other suitable sites.
8. Graft placement: Place the graft over the perforated area, ensuring it is securely positioned.
9. Securing the graft: Secure the graft with gelfoam or other suitable materials
Microscopic versus Endoscopic Myringoplasty:
The Advantages and Disadvantages
Microscopic Myringoplasty
Advantages
-
1. High magnification
Provides high-quality magnification, allowing for precise dissection and graft placement.
-
2. Wide availability
Microscopes are widely available in most operating rooms.
-
3. Established technique
Microscopic myringoplasty is a well-established technique with a long history of successful outcomes.
Disadvantages
-
1. Limited field of view
The microscope's field of view is limited, requiring frequent adjustments to visualize the entire surgical site.
-
2. Need for assistant
A skilled assistant is required to hold the microscope and adjust its position.
-
3. Potential for eye strain
Prolonged use of the microscope can cause eye strain for the surgeon.
Endoscopic Myringoplasty:
Advantages
-
1. Wide field of view
Endoscopes provide a wide field of view, allowing for better visualization of the surgical site.
-
2. Minimally invasive
Endoscopic myringoplasty is a minimally invasive technique, reducing trauma to surrounding tissues.
-
3. Reduced need for assistants
The endoscope can be held by the surgeon, reducing the need for assistants.
Disadvantages
-
1. Steep learning curve
Endoscopic myringoplasty requires specialized training and experience.
-
2. Equipment costs
Endoscopes and associated equipment can be expensive.
-
3. Potential for limited depth perception
Endoscopes can provide a two-dimensional view, potentially limiting depth perception.
Comparison of Outcomes
Studies comparing microscopic and endoscopic myringoplasty have shown:
-
Similar success rates
Both techniques have similar success rates in terms of graft uptake and hearing improvement.
-
Reduced operative time
Endoscopic myringoplasty may have shorter operative times compared to microscopic myringoplasty.
-
Less postoperative pain
Endoscopic myringoplasty may result in less postoperative pain and discomfort.
Ultimately, the choice between microscopic and endoscopic myringoplasty depends on the surgeon’s experience, the patient’s specific needs, and the available equipment.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
-
Tracheostomy
-
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
-
Acute Epiglottitis And Approach To Management
-
Synoptic Overview Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
Prioritizing Support For People With Disabilities Over Unhealthy Competitions That Marginalise The Downtrodden
-
Otitic Barotrauma
-
Titbits of Informed Consent Process for a Medical or Surgical Procedure
-
Comprehensive Overview of Mpox (Monkeypox)
-
Overview Of Corrosive Ingestion - Acid & Alkalis, and Management Approach
-
Ethical Conundrum
-
Comprehensive Overview of Laryngeal Papillomatosis and HPV Virus
-
All You Need To *Know About Gardasil*
-
Preauricular Sinus
-
Laryngomalacia - comprehensive overview
-
Flexible Laryngoscopy features of Laryngomalacia
-
Case Report of a Rare Cause of Upper Airway Obstruction In Adults
Categories
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.