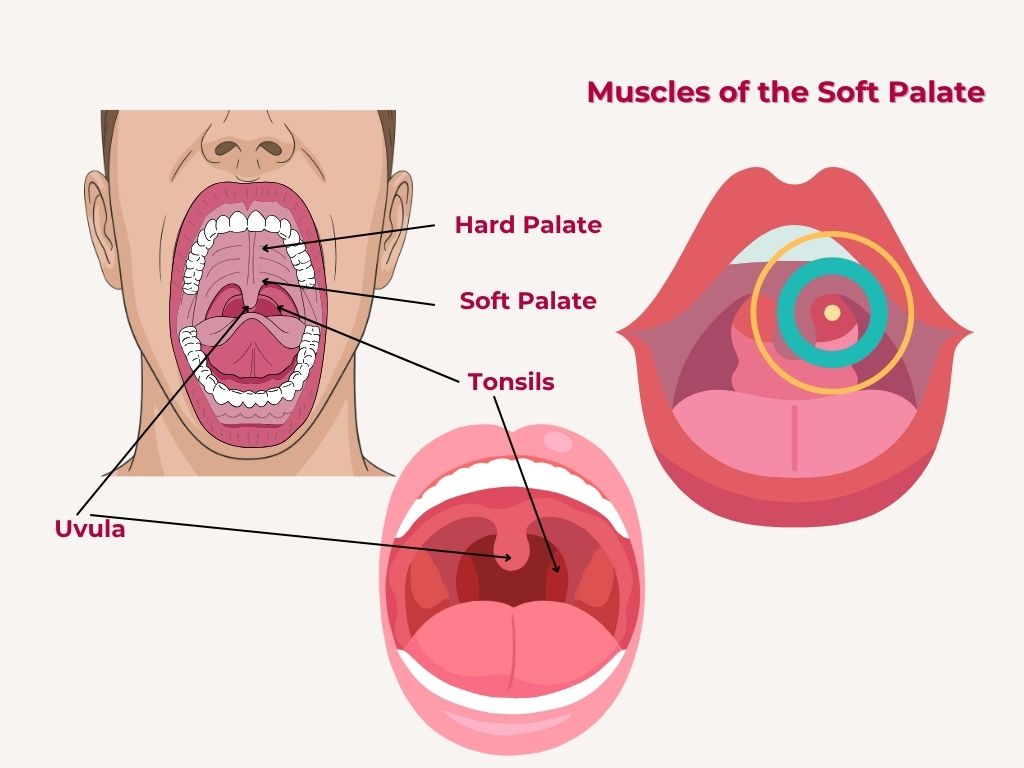
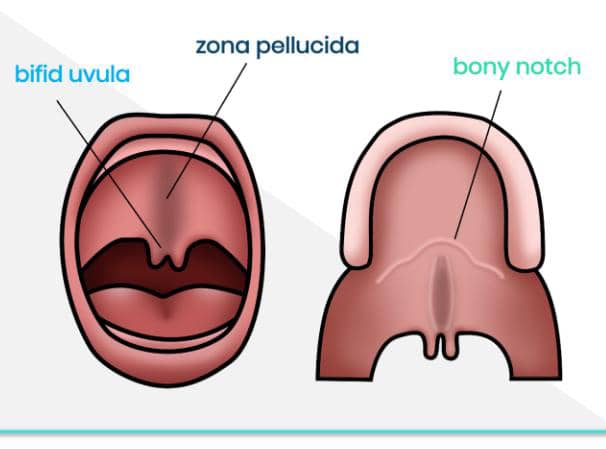
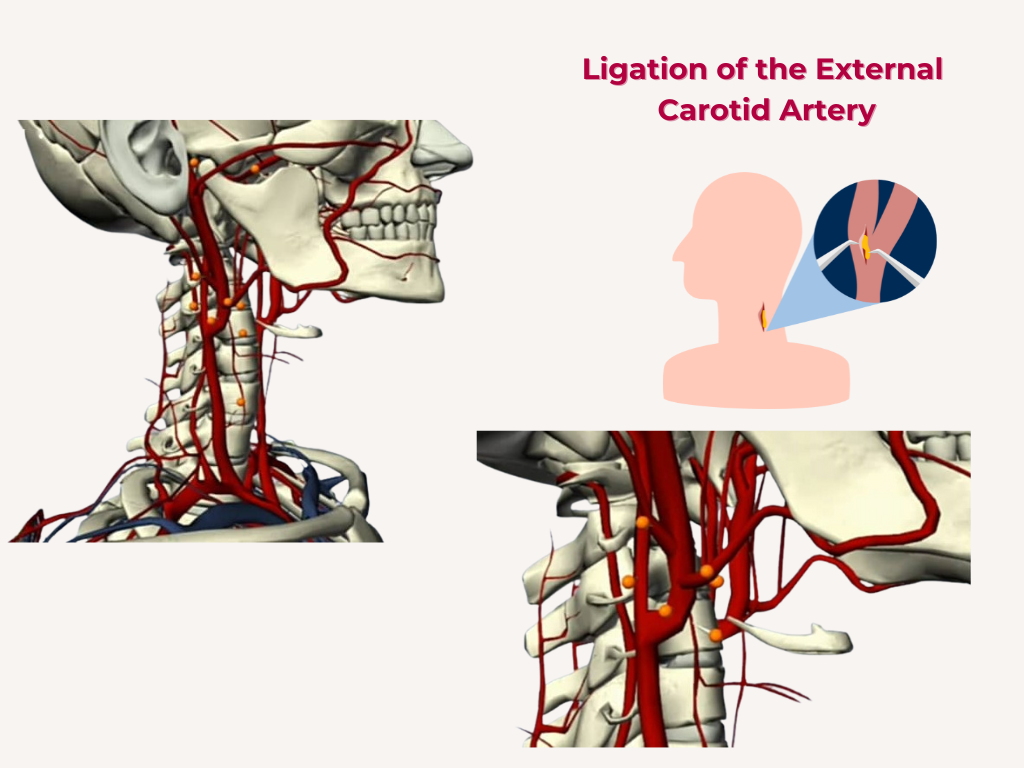
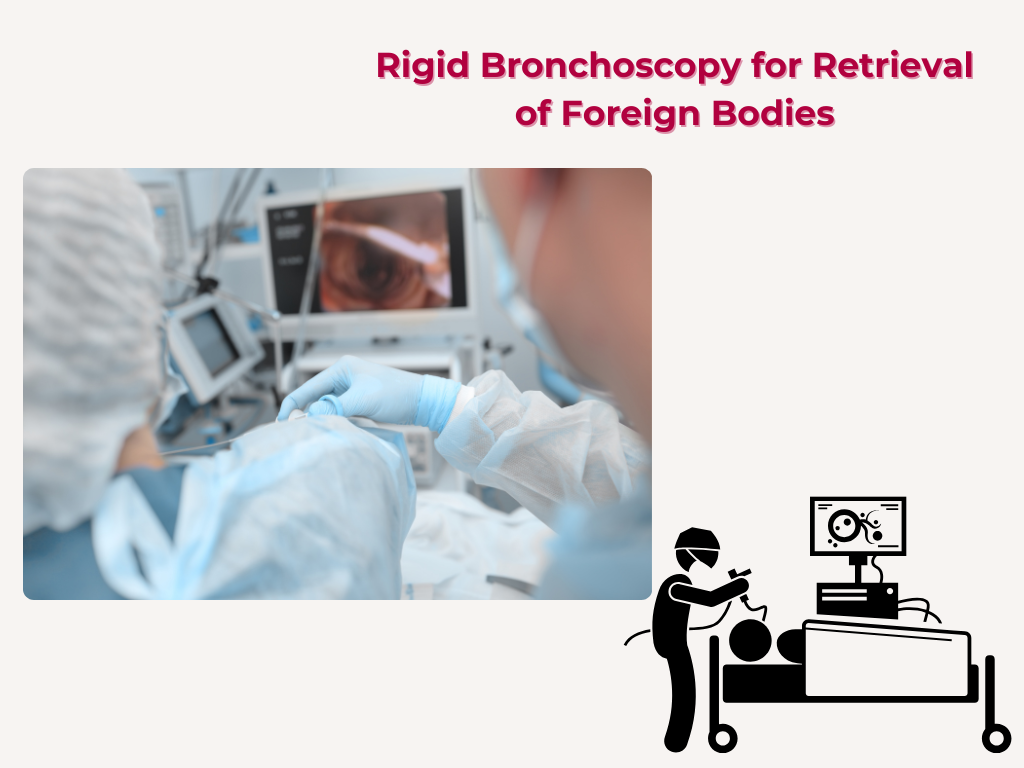
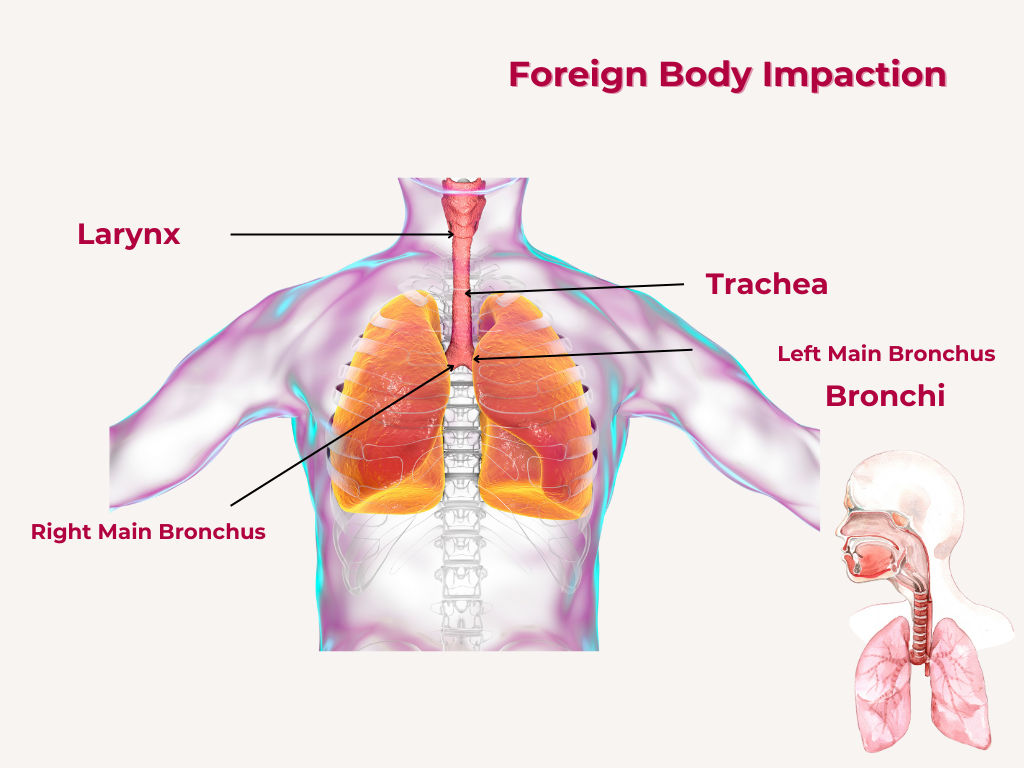
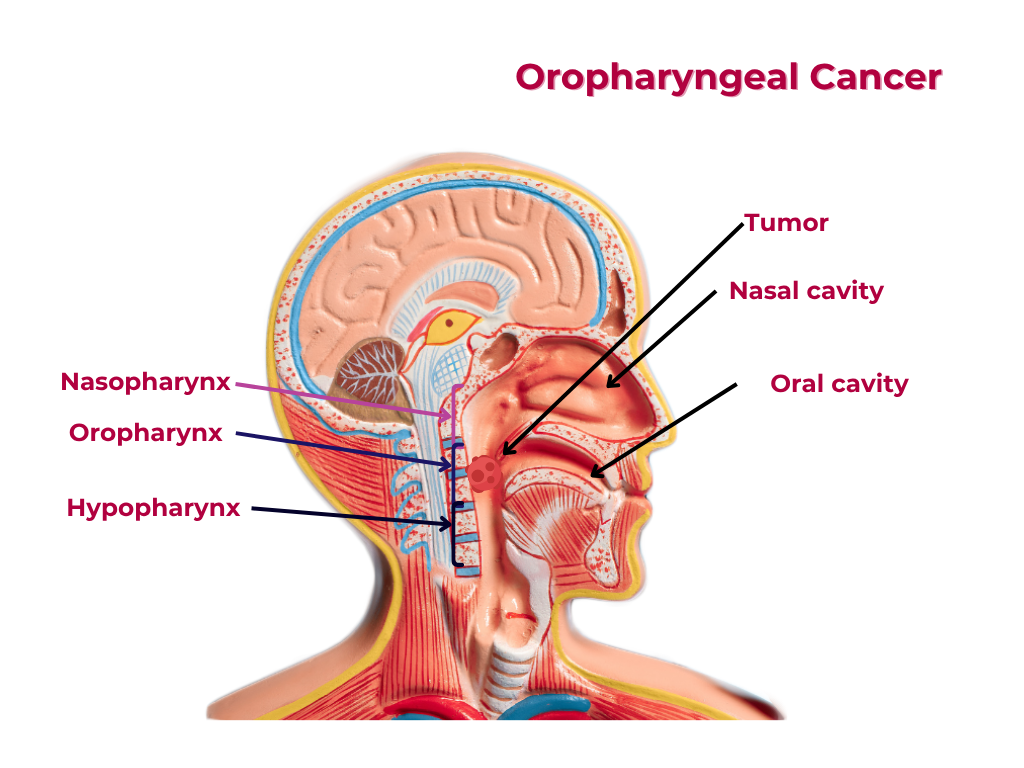
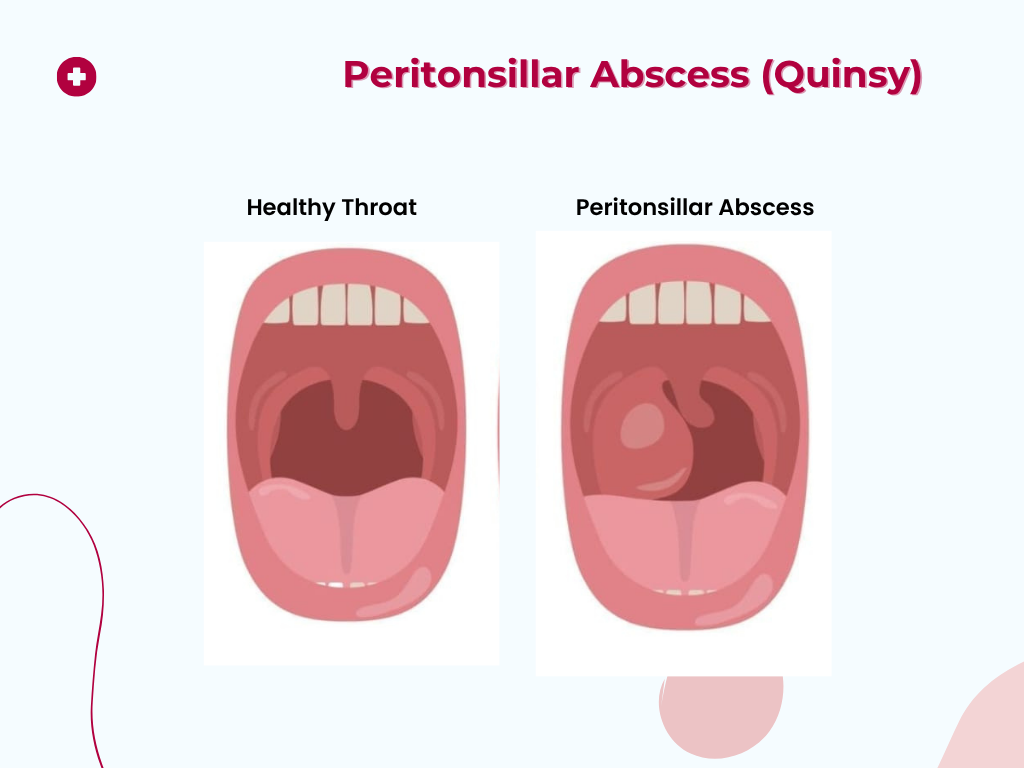
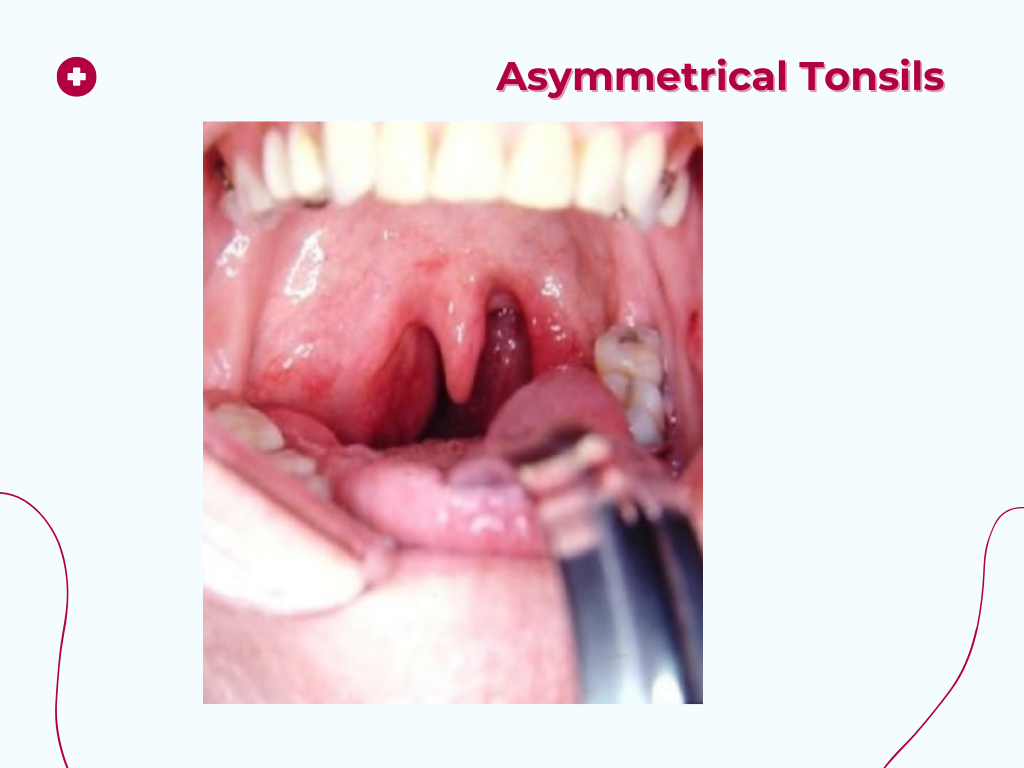
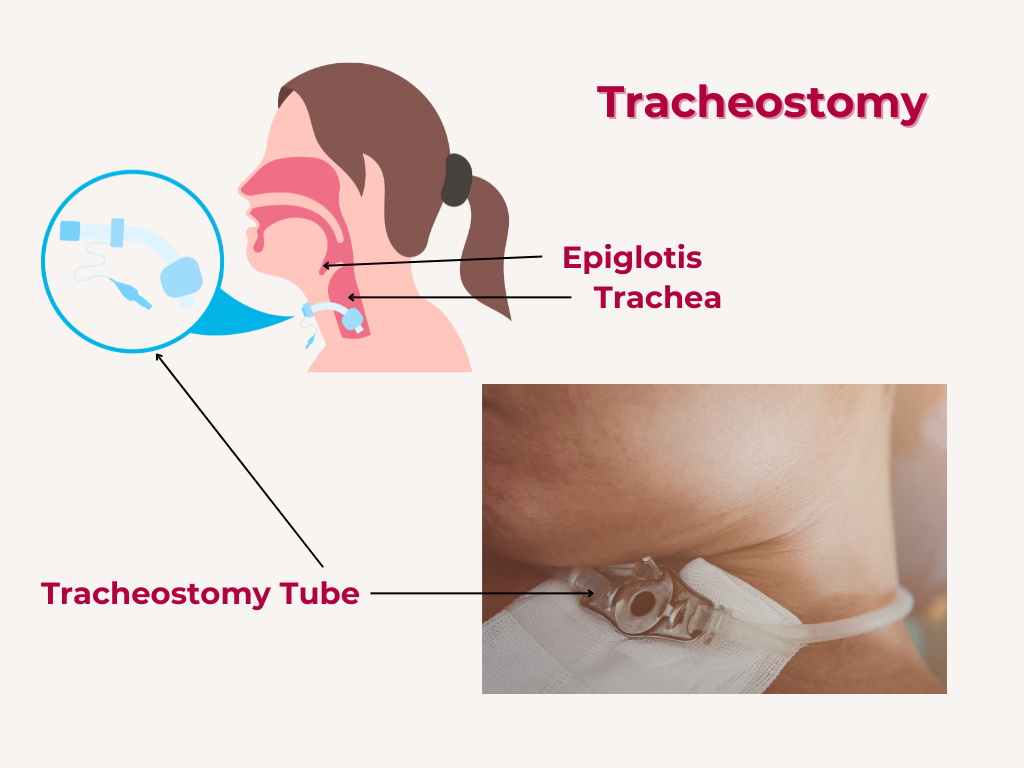
Nuggets of ORL-LARYNGOLOGY
Laryngology refers to a a specialized branch of otolaryngology (ENT) focused on diagnosing and treating disorders of the larynx (voice box), including the vocal cords, as well as related structures in the throat and upper airway.