Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
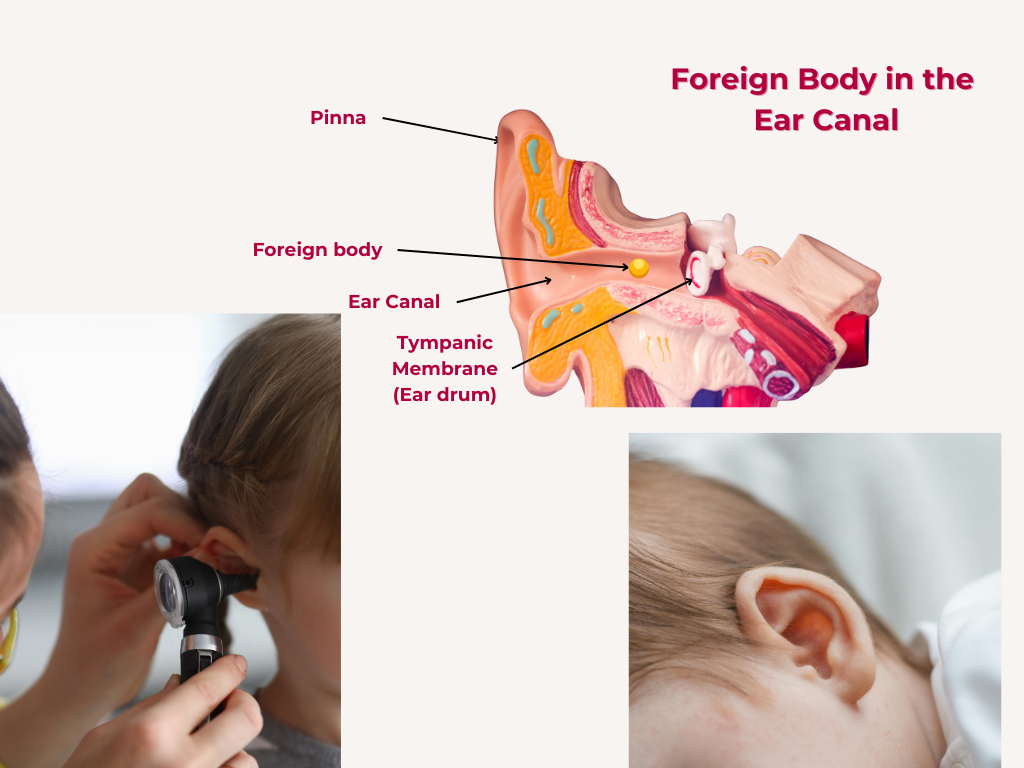
Overview
Insertion of foreign bodies into the ear canal is a common occurrence in children, often due to curiosity or accidental insertion. Managing such cases requires a careful approach to ensure safe and effective removal.
Anatomy of the Aural Cavity
The ear canal is a narrow, S-shaped passage that requires gentle manipulation to avoid causing damage.
Removal Under Local or General Anesthesia
The choice between local and general anesthesia depends on the child's age, cooperation, and the complexity of the procedure.
Removal Under Local Anesthesia
-
1. Setup
The child is seated upright, and the ear canal is anesthetized with a topical anesthetic.
-
2. Assistance
A parent or assistant may be needed to restrain the child.
-
3. Instruments
An otoscope and instruments like alligator forceps or a loop are used to visualize and remove the foreign body.

Risks of Removal Under Local Anesthesia
-
1. Discomfort
The child may experience discomfort or pain during the procedure.
-
2.Anxiety
The child may become anxious or uncooperative.
-
3. Failure to remove
The foreign body may not be successfully removed.
Step-by-Step Procedure of foreign body removal in the ear canal under general anaesthesia
-
1. Position
The child is positioned supine on the operating table.
-
2. Instruments
An otoscope and instruments like alligator forceps or a loop are used to visualize and remove the foreign body.
-
3. Procedure
The otoscope is used to visualize the foreign body, and the instrument is used to carefully grasp and remove it.
Complications
-
1. Ear canal trauma
Trauma to the ear canal can occur during the procedure.
-
2. Perforation of the tympanic membrane
The tympanic membrane may be perforated during the procedure.
-
3. Infection
Infection can occur if the foreign body is not removed promptly.
Removing a foreign body from the ear canal in a child requires a careful approach, and the choice of anesthesia depends on the individual case. With proper setup, instruments, and technique, successful removal can be achieved while minimizing complications.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Overview of AI Tools In Modern ORL Practice
-
Nuggets of ORL-LARYNGOLOGY
-
All You Need To Know About PET Scan
-
Nuggets of ORL-PAEDIATRICS
-
Nuggets of ORL-OTOLOGY
-
Nuggets of ORL-RHINOLOGY
-
Nuggets of Otorhinolaryngology-Basic sciences
-
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Soft Palate
-
Ethmoidal Arteries Ligation for Epistaxis
-
Submucous Cleft Palate (SMCP)
-
Approach to Ligation of the External Carotid Artery
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body in the nasal cavity.
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
-
Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation (ESPAL) for Epistaxis
-
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
-
Tracheostomy
Categories
RELATED POSTS
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.

