Anatomy of Oesophagus
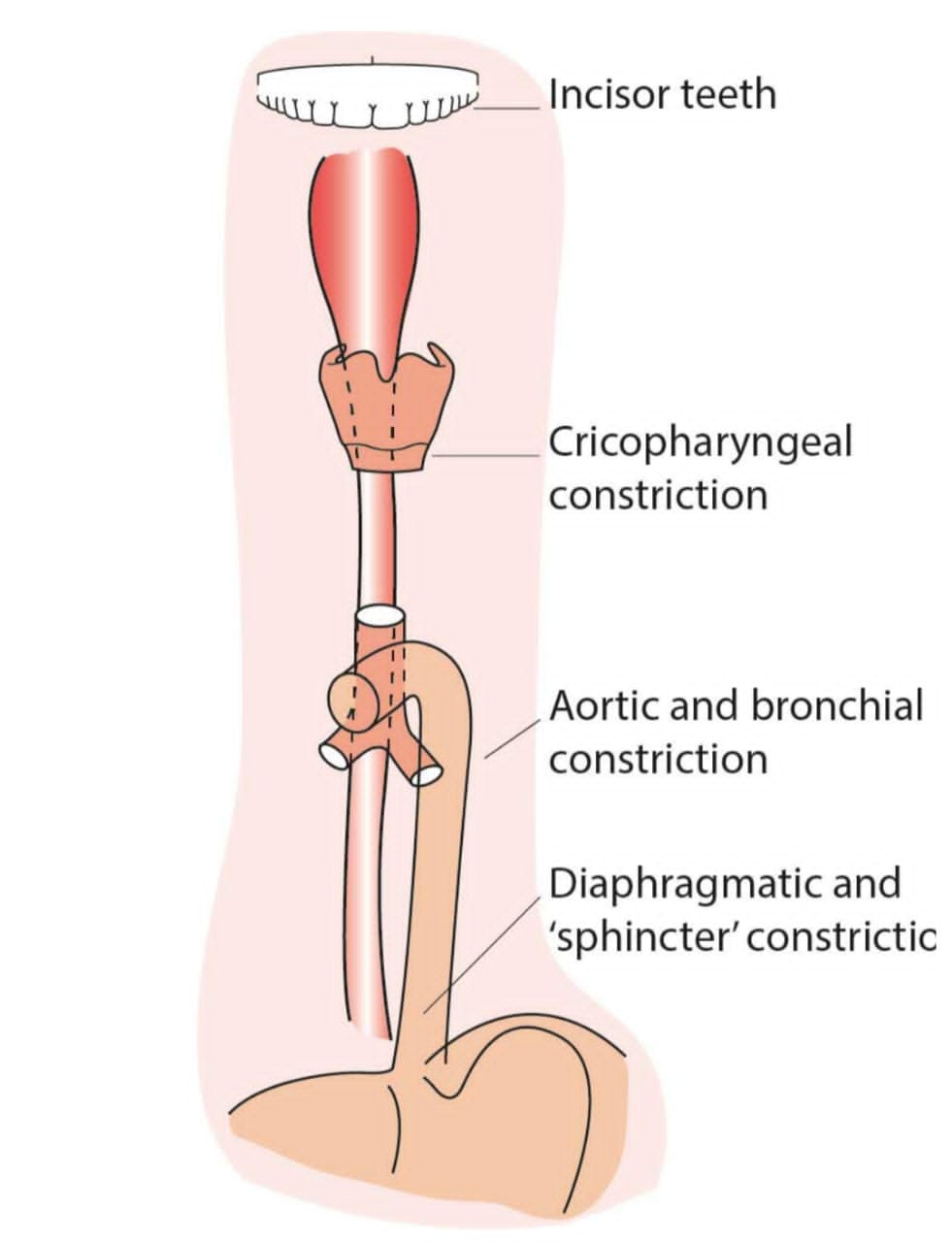
Anatomy of the Oesophagus
Oesophagus refers to the muscular tube that connect the throat to the stomach.
Length and Width of Oesophagus
-
Length:
The oesophagus is approximately 25-30 cm (10-12 inches) long in adults.
-
Width:
The oesophagus has a diameter of about 2-3 cm (0.8-1.2 inches), but it can vary depending on the location and the presence of any pathology.
Distances of Anatomical Constrictions of Oesophagus from Upper Incisor Teeth
Adults
- Lower oesophageal sphincter (cardia): approximately 37-40 cm (15-16 inches) from the upper incisors.
- Upper oesophageal sphincter (cricopharyngeus): approximately 15-17 cm (6-7 inches) from the upper incisors.
- Aortic arch constriction: approximately 22-25 cm (9-10 inches) from the upper incisors.
- Left mainstem bronchus constriction: approximately 25-27 cm (10-11 inches) from the upper incisors.
Children
The distances are shorter in children and vary depending on age and size.
Cross-Sectional Layers of Wall of Oesophagus
-
1. Mucosa:
The innermost layer, consisting of epithelial cells and lamina propria.
-
2. Submucosa:
A layer of loose connective tissue beneath the mucosa.
-
3. Muscularis propria:
A layer of smooth muscle, divided into inner circular and outer longitudinal layers.
-
4. Adventitia:
The outermost layer, consisting of connective tissue.
Segmental Blood Supply
-
1. Upper oesophagus:
Blood supply from the inferior thyroid arteries.
-
2. Middle oesophagus:
Blood supply from the bronchial arteries and oesophageal branches of the aorta.
-
3. Lower oesophagus:
Blood supply from the left gastric arteries and oesophageal branches of the aorta
Nerve Supply
-
Parasympathetic:
Vagus nerve (cranial nerve X) provides parasympathetic innervation.
-
Sympathetic:
Sympathetic nerves from the thoracic sympathetic trunk provide sympathetic innervation.
Clinical Notes on Trauma to the Oesophagus
-
Traumatic injuries:
Can be caused by penetrating trauma, blunt trauma, or iatrogenic injuries (e.g., during endoscopy).
-
Indications for total oesophagectomy:
May be considered in cases of severe oesophageal trauma, oesophageal cancer, or other conditions that render the oesophagus non-functional.
When to Repair Traumatic Injury to the Oesophagus
-
Early repair:
Ideally, traumatic injuries to the oesophagus should be repaired within 24 hours to minimize the risk of complications.
-
Delayed repair:
May be considered in cases where the patient is unstable or the injury is not immediately life-threatening.
Understanding the anatomy of the oesophagus is crucial for diagnosing and managing oesophageal disorders, including traumatic injuries. Prompt recognition and treatment of oesophageal trauma can help prevent complications and improve patient outcomes.
Want to Know
The medical procedure that involves the insertion of a rigid tube with a light and camera (oesophagoscope) into the oesophagus to visualize, diagnose, and treat various oesophageal conditions.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Nuggets of ORL-OTOLOGY
-
Nuggets of ORL-RHINOLOGY
-
Nuggets of Otorhinolaryngology-Basic sciences
-
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Soft Palate
-
Ethmoidal Arteries Ligation for Epistaxis
-
Submucous Cleft Palate (SMCP)
-
Approach to Ligation of the External Carotid Artery
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body in the nasal cavity.
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
-
Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation (ESPAL) for Epistaxis
-
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
-
Tracheostomy
-
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
-
Acute Epiglottitis And Approach To Management
-
Synoptic Overview Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
Prioritizing Support For People With Disabilities Over Unhealthy Competitions That Marginalise The Downtrodden
-
Otitic Barotrauma
-
Titbits of Informed Consent Process for a Medical or Surgical Procedure
-
Comprehensive Overview of Mpox (Monkeypox)
-
Overview Of Corrosive Ingestion - Acid & Alkalis, and Management Approach
-
Ethical Conundrum
Categories
RELATED POSTS
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.

