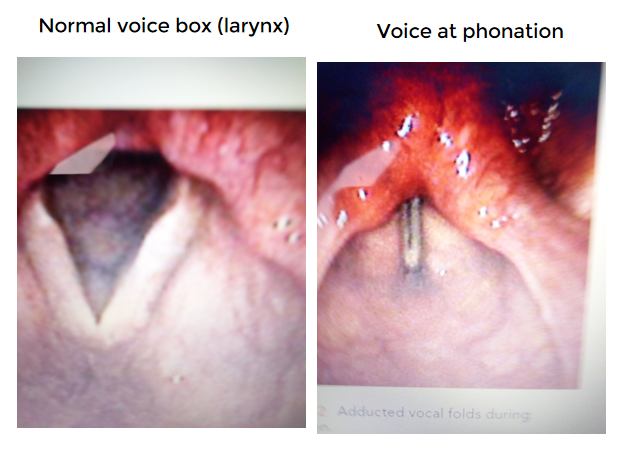
As everyone’s voice is unique it is difficult to define a normal voice. A normal voice is pleasant sounding and has age and sex appropriate pitch and loudness. When a voice is not pleasant sounding, is too loud or too soft or is too high or low for one’s gender, a voice problem MAY be present. A phonation disorder causes the voice to sound breathy, hoarse, husky, or strained and Resonance disorders are hypernasality or hyponasality.
Voice disorders are divided into 2 categories: organic voice disorders and functional voice disorders.
Causes of Organic Voice Disorders
- Laryngeal web
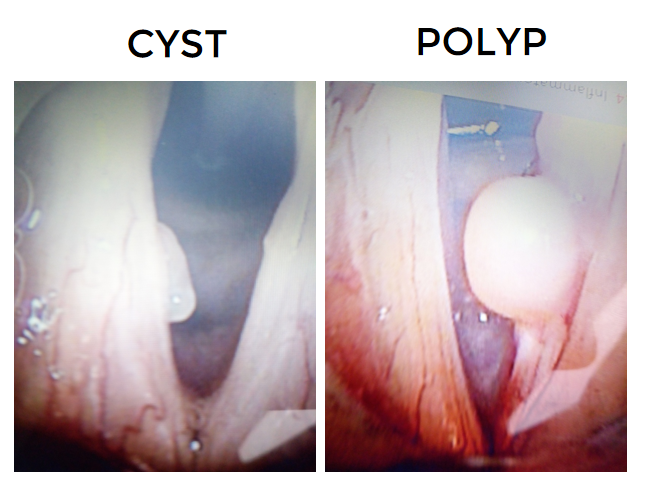
- Vocal cord cyst
- Vocal cord polyp
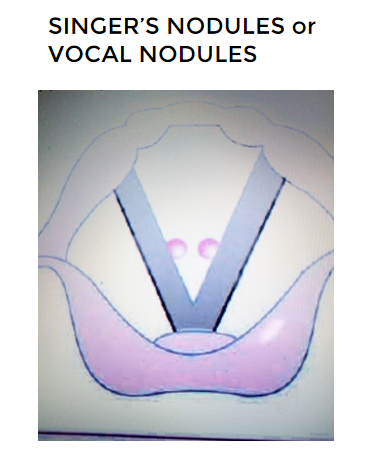
- SINGER’S NODE
- Granuloma
- Hemangioma
- Papilloma
- Vocal fold paralysis
- Endocrine changes
- CANCER OF THE LARYNX
Functional Voice Disorders
From improper voice use.
Voice Misuse
- talking too much or too loudly
- yelling
- using an unnatural pitch (faking a deep or high voice).
Voice Abuse (nonverbal vocal behavior)
- excessive throat clearing
- laughing
- crying
- coughing
- smoking
Voice Misuse and Abuse result in physiological changes to the vocal folds. Creating vocal nodules, polyps, contact ulcers, oedema
The therapy for functional disorders are:
- Identifying abuses and misuses
- Reducing or eliminating them (causes)
- Rule out an organic basis before starting voice therapy.
Anyone who has persistent hoarseness of voice for more than 3 weeks must see an ENT specialist for evaluation: Organic or functional?
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
Categories
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.