Tympanometry
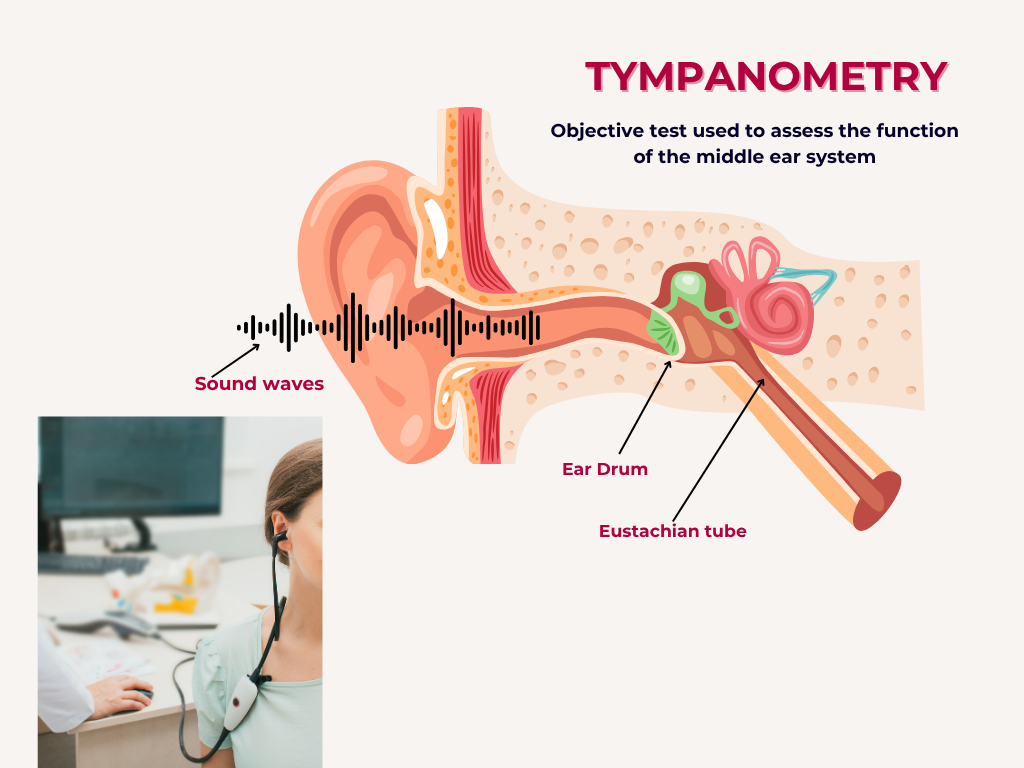
Tympanometry is an objective test used to assess the function of the middle ear system. It measures the movement of the eardrum (tympanic membrane) and the reflexes of the middle ear muscles in response to changes in air pressure.
Tympanometer
A tympanometer is a device used to perform tympanometry. It consists of a probe that is inserted into the ear canal and a pump that changes the air pressure in the ear canal. The device measures the movement of the eardrum and the reflexes of the middle ear muscles.
Types of Tympanograms
Tympanograms are classified into several types based on the shape and characteristics of the tympanogram curve.
The main types are:
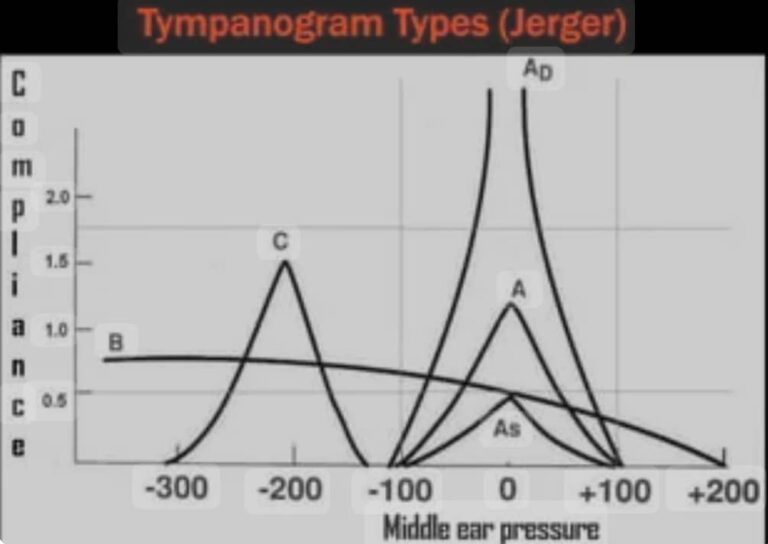
Type A
Normal tympanogram with a single peak, indicating normal middle ear function.
-
Type Ad (High Compliance)
Tympanogram with a high peak, indicating hypermobility of the tympanic membrane or ossicular discontinuity.
-
Type As (Low Compliance)
Tympanogram with a low peak, indicating fixation of the ossicles (e.g., otosclerosis).
Type B
Flat tympanogram, indicating little or no movement of the tympanic membrane, often seen in:
- Middle ear fluid (otitis media with effusion)
- Tympanic membrane perforation
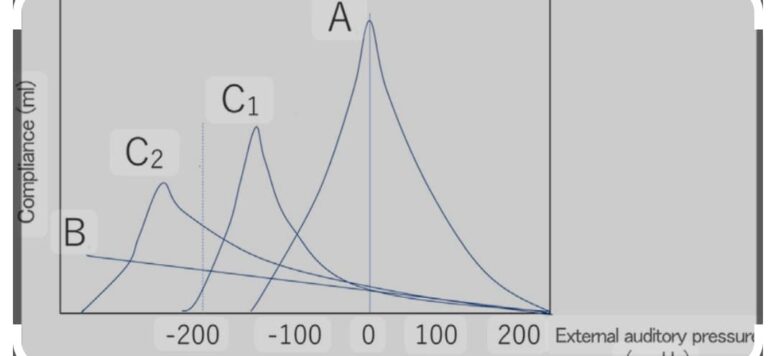
Type C
Tympanogram with a peak in the negative pressure range, indicating Eustachian tube dysfunction and negative middle ear pressure.
Pressure ranges for the different types C tympanograms:
Here are the typical pressure ranges for the different types of Type C tympanograms:
-
Type C1 Tympanogram
- Pressure range: -100 daPa to -150 daPa
- Significance: Mild negative pressure, may indicate mild Eustachian tube dysfunction or middle ear fluid. -
Type C2 Tympanogram
- Pressure range: -150 daPa to -250 daPa
- Significance: Moderate negative pressure, may indicate moderate Eustachian tube dysfunction, middle ear fluid, or a blocked Eustachian tube. -
Type C3 Tympanogram
- Pressure range: -250 daPa to -350 daPa
- Significance: Severe negative pressure, may indicate severe Eustachian tube dysfunction, chronic middle ear fluid, or a blocked Eustachian tube. -
Type C4 Tympanogram
- Pressure range: -350 daPa to -450 daPa
- Significance: Very deep negative pressure, may indicate a retracted tympanic membrane, a blocked Eustachian tube, or chronic middle ear fluid. -
Type C5 Tympanogram
- Pressure range: -450 daPa or lower - Significance: Extremely deep negative pressure, may indicate a perforated tympanic membrane, middle ear fluid, or a blocked Eustachian tube.
Keep in mind that these pressure ranges are general guidelines and may vary depending on the specific tympanometer and testing conditions.
NOTE:
- daPa stands for decapascals, which is a unit of pressure.
- A tympanogram with a peak in the positive range is not typically seen in normal middle ear function or common middle ear disorders.
However, it’s worth noting that.
Patulous Eustachian Tube
In some cases, a patulous Eustachian tube (a condition where the Eustachian tube remains abnormally open) might result in a tympanogram with a peak in the positive pressure range or an unusually wide tympanogram. However, this is not a definitive indicator.
Other Considerations
Tympanogram results should be interpreted in conjunction with other diagnostic tests and clinical findings to determine the underlying condition. If you have specific questions or concerns about tympanometry or middle ear function, consult a qualified healthcare professional.
These classifications help audiologists and ENT specialists diagnose and manage middle ear disorders
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Nuggets of ORL-OTOLOGY
-
Nuggets of ORL-RHINOLOGY
-
Nuggets of Otorhinolaryngology-Basic sciences
-
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Soft Palate
-
Ethmoidal Arteries Ligation for Epistaxis
-
Submucous Cleft Palate (SMCP)
-
Approach to Ligation of the External Carotid Artery
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body in the nasal cavity.
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
-
Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation (ESPAL) for Epistaxis
-
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
Categories
RELATED POSTS
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.