Orbital complications of rhinosinusitis
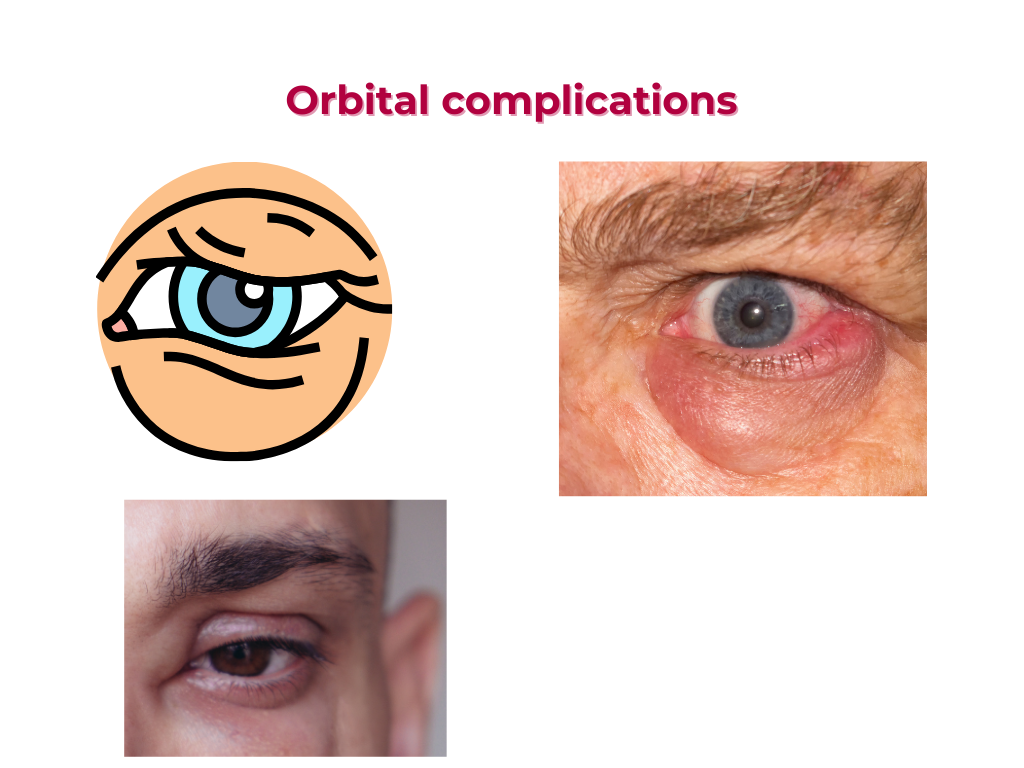
Orbital complications of rhinosinusitis can be severe and potentially vision-threatening. Here’s an outline of the complications and their management:
Classification of Orbital Complications
1. Preseptal cellulitis: Inflammation of the eyelid and surrounding tissues.
2. Orbital cellulitis: Infection of the orbital tissues, including the fat, muscles, and blood vessels.
3. Subperiosteal abscess: Collection of pus between the bone and periosteum.
4. Orbital abscess: Collection of pus within the orbit.
5. Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Blood clot formation in the cavernous sinus.
Clinical Presentation
1. Preseptal cellulitis: Eyelid swelling, redness, and warmth.
2. Orbital cellulitis: Proptosis (bulging of the eye), limited eye movement, and pain.
3. Subperiosteal abscess: Proptosis, limited eye movement, and pain.
4. Orbital abscess: Severe proptosis, limited eye movement, and pain.
5. Cavernous sinus thrombosis: Bilateral proptosis, limited eye movement, and cranial nerve deficits.
Diagnostic Evaluation
1. Imaging studies: Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans to evaluate the extent of disease and identify complications.
2. Laboratory tests: Blood cultures, complete blood count, and erythrocyte sedimentation rate.
3. Ophthalmologic evaluation: Visual acuity, intraocular pressure, and slit-lamp examination.
Management of rhinosinusitis.
Medical Management
1. Antibiotics: Broad-spectrum antibiotics to cover Streptococcus, Staphylococcus, and anaerobic bacteria.
2. Corticosteroids: To reduce inflammation and swelling.
3. Pain management: Analgesics to manage pain and discomfort.
Surgical Management
1. Endoscopic sinus surgery: To drain the sinuses and remove infected tissue..
2. Orbital surgery: To drain abscesses, relieve pressure, and restore vision.
3. Cavernous sinus thrombectomy: To remove the blood clot and restore blood flow.
Complications and Prognosis
-
1. Vision loss
Permanent vision loss can occur if treatment is delayed or inadequate.
-
2. Chronic sinusitis:
Recurrent or persistent sinusitis can occur if underlying conditions are not addressed.
-
3. Intracranial complications:
Meningitis, brain abscess, or stroke can occur if the infection spreads to the brain.
Prompt recognition and management of orbital complications of rhinosinusitis are essential to prevent long-term vision loss and other serious complications.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
-
Acute Epiglottitis And Approach To Management
-
Synoptic Overview Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
Prioritizing Support For People With Disabilities Over Unhealthy Competitions That Marginalise The Downtrodden
-
Otitic Barotrauma
-
Titbits of Informed Consent Process for a Medical or Surgical Procedure
-
Comprehensive Overview of Mpox (Monkeypox)
-
Overview Of Corrosive Ingestion - Acid & Alkalis, and Management Approach
-
Ethical Conundrum
-
Comprehensive Overview of Laryngeal Papillomatosis and HPV Virus
-
All You Need To *Know About Gardasil*
-
Preauricular Sinus
-
Laryngomalacia - comprehensive overview
-
Flexible Laryngoscopy features of Laryngomalacia
-
Case Report of a Rare Cause of Upper Airway Obstruction In Adults
-
Usefulness of The Neck Soft Tissues X-Ray
-
Paranasal Sinuses Radiology
-
Swallow Function Test
-
Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy In Head And Neck Cancers
-
Myringoplasty
-
Overview of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM)
Categories
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.

