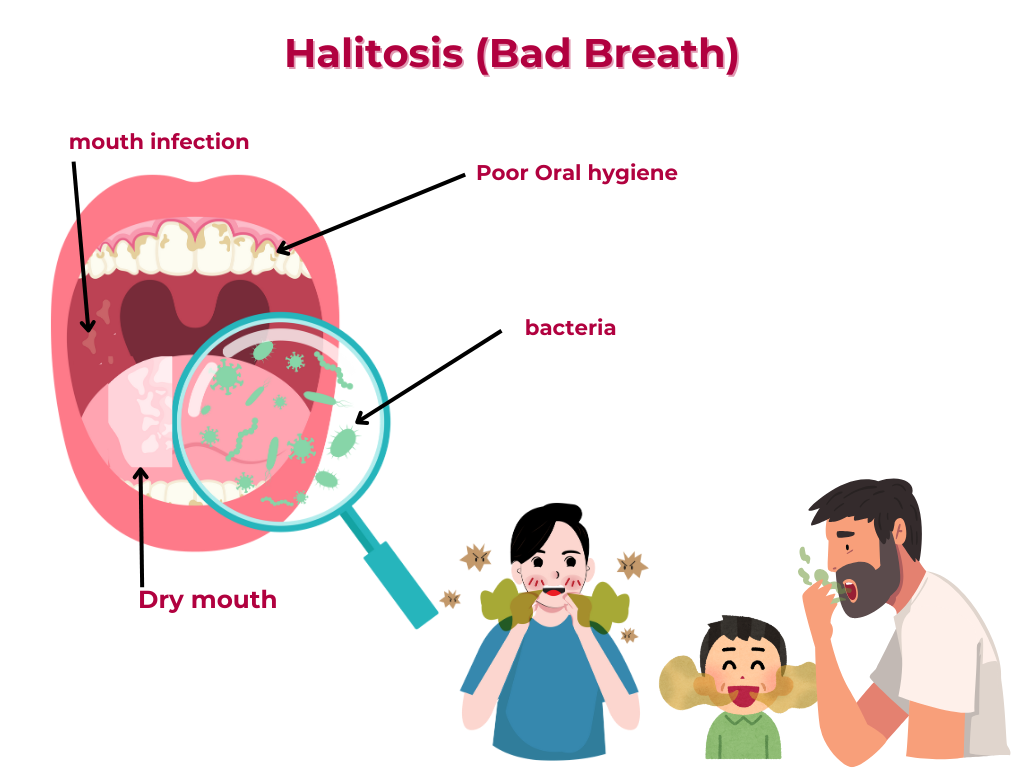
Halitosis, also known as bad breath, is a common condition characterized by an unpleasant odor emanating from the mouth.
It affects approximately 20-30% of the global population.
Aetiology
Halitosis can be caused by various factors, including:
-
Poor oral hygiene
Inadequate brushing, flossing, and tongue cleaning.
-
Gingivitis and periodontitis
Gum diseases that can cause bad breath.
-
Tongue coating
Accumulation of bacteria, dead cells, and debris on the tongue surface.
-
Dry mouth (xerostomia)
Reduced saliva production, which can lead to bacterial overgrowth.
-
Respiratory infections
Pneumonia, bronchitis, and sinusitis can cause bad breath.
-
Gastrointestinal disorders
Gastroesophageal reflux disease (GERD), irritable bowel syndrome (IBS), and small intestine bacterial overgrowth (SIBO).
-
Systemic diseases
Diabetes, liver or kidney disease, and certain medications.
-
Diet
Consuming foods with strong odors, such as garlic, onions, or fish.
-
Smoking and tobacco use
Can cause dry mouth and increase bacterial growth.
Diagnosis
To diagnose halitosis, a healthcare professional will:
-
Take a thorough medical history
To identify underlying conditions that may be contributing to bad breath.
-
Perform an oral examination:
To assess oral hygiene, gum health, and tongue coating.
-
Use a halimeter
A device that measures the concentration of volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) in the mouth.
-
Conduct a tongue coating assessment
To evaluate the presence and severity of tongue coating.
Management
Treatment of halitosis depends on the underlying cause, but may include:
- Improved oral hygiene: Regular brushing, flossing, and tongue cleaning.
- Professional dental cleaning: To remove plaque, tartar, and bacteria.
- Antibacterial mouthwashes: To reduce bacterial growth and VSC production.
- Tongue cleaning and scraping: To remove tongue coating and debris.
- Saliva stimulants: To increase saliva production and help wash away bacteria.
- Treatment of underlying conditions: Such as gum disease, respiratory infections, or gastrointestinal disorders.
- Dietary changes: Avoiding foods with strong odors and increasing water intake.
- Smoking cessation: To reduce dry mouth and bacterial growth.
Complications
If left untreated, halitosis can lead to:
-
Social and emotional distress
Bad breath can cause embarrassment, anxiety, and depression.
-
Poor oral health
Untreated gum disease and tooth decay can lead to more severe oral health issues.
-
Systemic diseases
Untreated underlying conditions, such as diabetes or gastrointestinal disorders, can lead to more severe complications.
What Are Saliva Stimulants?
Saliva stimulants are substances or products that help increase saliva production in the mouth. They are often used to alleviate dry mouth (xerostomia) and promote oral health. Here are some common saliva stimulants:
Medications
- Pilocarpine: A prescription medication that stimulates saliva production.
- Cevimeline: A prescription medication that increases saliva production.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Products
-
Saliva substitutes
Products like Mouth Kote, Salivart, or Xerolube that mimic the natural properties of saliva.
-
Saliva stimulant sprays
Sprays like SalivaMAX or Orajel that contain ingredients like xylitol or citric acid to stimulate saliva production.
-
Chewing gums
Sugar-free chewing gums like Spry or Xylitol that stimulate saliva production and help clean teeth.
Natural Saliva Stimulants
-
Citrus fruits
Oranges, lemons, or limes can stimulate saliva production due to their acidity.
-
Ginger
Chewing ginger or drinking ginger tea can help stimulate saliva production.
-
Green tea
Drinking green tea may help stimulate saliva production due to its antioxidant properties.
-
Xylitol
A natural sweetener that can stimulate saliva production and prevent tooth decay.
Other Options
- Acupuncture: Some studies suggest that acupuncture can help stimulate saliva production.
- Oral exercises: Certain oral exercises, like tongue stretching or lip exercises, may help stimulate saliva production.
It’s essential to consult with a healthcare professional before using any saliva stimulants, especially if you have underlying medical conditions or take medications.
What are Volatile Sulphur Compounds (Vsc)?
Volatile sulfur compounds (VSCs) are a group of chemicals that contain sulfur and are responsible for the characteristic odor of bad breath (halitosis). These compounds are produced by the breakdown of food particles, especially proteins, by bacteria in the mouth.
Types of VSCs
- Hydrogen sulfide (H2S): A gas with a characteristic “rotten egg” odor.
- Methyl mercaptan (CH3SH): A gas with a strong, unpleasant odor.
- Dimethyl sulfide (CH3SCH3): A gas with a sweet, unpleasant odor.
Sources of VSCs
-
Oral bacteria
Bacteria in the mouth, especially on the tongue and in the gingival crevice, break down food particles and produce VSCs.
-
Food particles
Trapped food particles, especially proteins, can be broken down by bacteria and produce VSCs.
-
Gingivitis and periodontitis
Gum diseases can lead to an increase in VSC-producing bacteria.
-
Dry mouth
A lack of saliva can contribute to an increase in VSCs.
-
Tongue coating
A thick, white coating on the tongue can harbor VSC-producing bacteria.
Detection of VSCs
- Halimeter: A device that measures the concentration of VSCs in the mouth.
- Gas chromatography: A laboratory test that can detect and quantify VSCs.
Management of VSCs
-
Good oral hygiene
Regular brushing, flossing, and tongue cleaning can help reduce VSC-producing bacteria.
-
Antibacterial mouthwashes
Mouthwashes containing ingredients like chlorine dioxide or essential oils can help reduce VSC-producing bacteria.
-
Tongue cleaning
Regular tongue cleaning can help remove VSC-producing bacteria and reduce bad breath.
-
Saliva stimulants
Chewing sugar-free gum or sucking on sugar-free candies can stimulate saliva production and help wash away VSC-producing bacteria.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
-
Acute Epiglottitis And Approach To Management
-
Synoptic Overview Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
Prioritizing Support For People With Disabilities Over Unhealthy Competitions That Marginalise The Downtrodden
-
Otitic Barotrauma
-
Titbits of Informed Consent Process for a Medical or Surgical Procedure
-
Comprehensive Overview of Mpox (Monkeypox)
-
Overview Of Corrosive Ingestion - Acid & Alkalis, and Management Approach
-
Ethical Conundrum
-
Comprehensive Overview of Laryngeal Papillomatosis and HPV Virus
-
All You Need To *Know About Gardasil*
-
Preauricular Sinus
-
Laryngomalacia - comprehensive overview
-
Flexible Laryngoscopy features of Laryngomalacia
-
Case Report of a Rare Cause of Upper Airway Obstruction In Adults
-
Usefulness of The Neck Soft Tissues X-Ray
-
Paranasal Sinuses Radiology
-
Swallow Function Test
-
Radiotherapy and Chemotherapy In Head And Neck Cancers
-
Myringoplasty
-
Overview of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM)
Categories
RELATED POSTS
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.