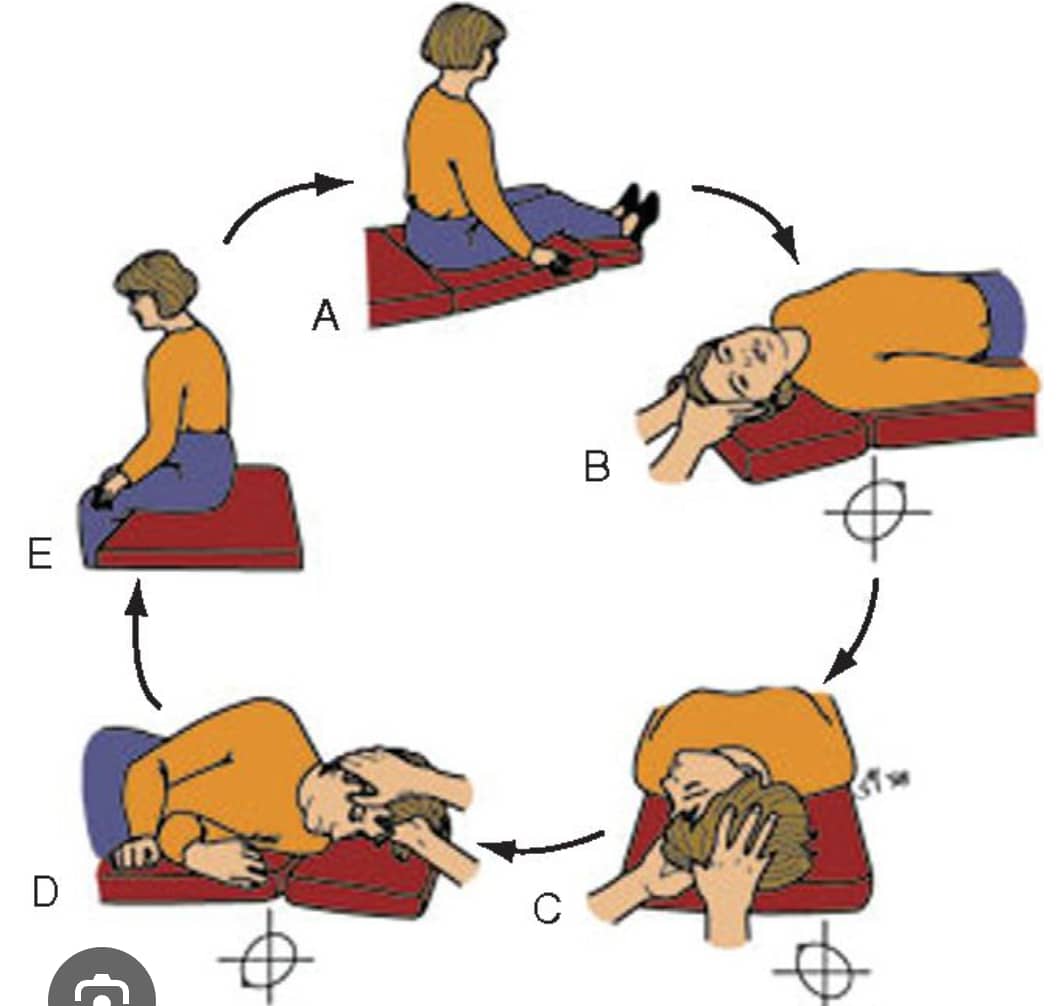
Epley’s maneuver, also known as the canalith repositioning procedure (CRP), is a series of specific head and body movements designed to treat benign paroxysmal positional vertigo (BPPV).
The following is a comprehensive overview of EPLEY’S manoeuvre:
What is BPPV?
-
Definition
BPPV is a vestibular disorder characterized by brief, intense episodes of vertigo triggered by specific head movements.
-
Causes
BPPV is caused by the movement of small calcium particles (otoconia) in the inner ear canals.
How Does Epley's Maneuver Work?
-
Goal
The goal of Epley's maneuver is to move the otoconia out of the inner ear canals and into a part of the ear where they won't cause symptoms.
-
Series of movements
The maneuver involves a series of specific head and body movements, which help to guide the otoconia out of the canals.
Steps of Epley's Maneuver
Step 1: Sit upright with your back straight.
Step 2: Lie down on your back with your head turned to the affected side (the side that triggers the vertigo).
Step 3: Wait for 30 seconds to allow the otoconia to move.
Step 4: Roll onto your side, keeping your head in the same position.
Step 5: Wait for 30 seconds.
Step 6: Sit up and then stand up.
Precautions and Contraindications
-
Precautions
If you have a history of neck or back problems, or if you're experiencing severe vertigo, consult with your healthcare provider before performing Epley's maneuver.
-
Contraindications
Epley's maneuver is not recommended for people with certain medical conditions, such as a recent stroke, brain injury.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
-
Tracheostomy
-
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
-
Acute Epiglottitis And Approach To Management
-
Synoptic Overview Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
Prioritizing Support For People With Disabilities Over Unhealthy Competitions That Marginalise The Downtrodden
-
Otitic Barotrauma
Categories
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.