Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
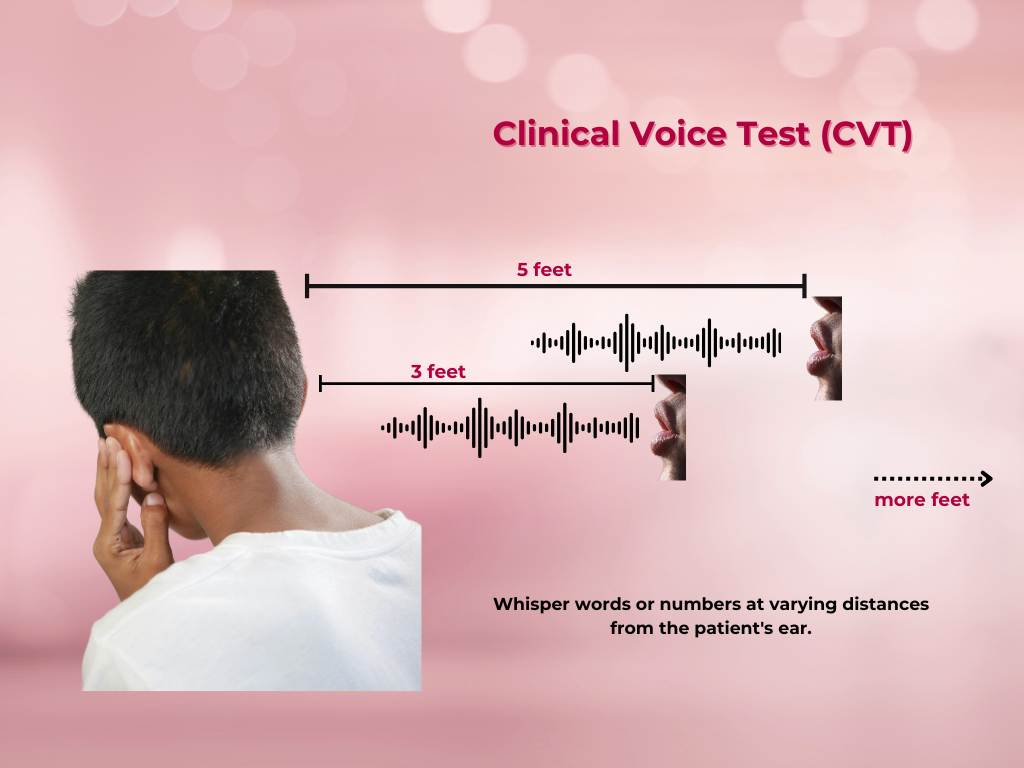
What is Clinical Voice Test (CVT)?
The Clinical Voice Test (CVT) is a simple, bedside test used to assess hearing loss. It involves whispering words or numbers at varying distances from the patient’s ear to estimate their hearing threshold.
The CVT relies on the patient’s ability to repeat whispered words or numbers accurately. The test assumes that a person with normal hearing can detect and repeat whispered sounds at a certain distance.
Step-by-Step Approach to CVT
Prepare the patient:
Ensure the patient is comfortable and understands the test.
Choose words or numbers( spondee words or bi-syllable words or numbers):
Select a set of words or numbers to whisper.
-
Note On Spondee Words Or Numbers:
Spondee words are words with two syllables that are pronounced with equal stress on both syllables.
Examples include:
- Hotdog
- Mousetrap
- Birthday
- Sunset
- Football
- Forty
- Eighteen
- Fifteen
These words are often used in audiology and speech therapy to assess speech perception and hearing thresholds.
Start at a distance:
Begin whispering at a distance of about 6 meters (20 feet) from the patient.
Gradually move closer:
Move closer to the patient, whispering the words or numbers, and ask them to repeat what they hear
Note the distance:
Note the distance at which the patient can accurately repeat the words or numbers.
Interpretation of Findings
-
1. Normal hearing:
If the patient can repeat whispered words or numbers at a distance of 6 meters (20 feet) or more, their hearing is likely normal.
-
2. Mild hearing loss:
If the patient can repeat whispered words or numbers at a distance of 3-6 meters (10-20 feet), they may have mild hearing loss.
-
3. Moderate hearing loss:
If the patient can repeat whispered words or numbers at a distance of 1-3 meters (3-10 feet), they may have moderate hearing loss.
-
4. Severe hearing loss:
If the patient cannot repeat whispered words or numbers even at close range (<1 meter or 3 feet), they may have severe hearing loss.
Conclusion
The Clinical Voice Test is a simple, non-invasive screening tool for hearing loss. While it is not a substitute for formal audiologic evaluation, it can provide a useful estimate of a patient's hearing status and guide further assessment or referral.
Alternative CVT Using Whispered Voice, Conversation Voice And Loud Voice
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) can be performed using whispered voice, conversation voice, and loud voice
Whispered Voice Test
-
1. Distance:
Typically performed at a distance of 6 meters (20 feet).
-
2. Voice level:
Whispered voice, without using vocal cords.
-
3. Interpretation:
If the patient can repeat words or numbers correctly, their hearing is likely normal.
Conversation Voice Test
-
1. Distance:
Typically performed at a distance of 1-2 meters (3-6 feet).
-
2. Voice level:
Normal conversation voice.
-
3. Interpretation:
If the patient can repeat words or numbers correctly, their hearing is likely within normal limits for conversational speech.
Loud Voice Test
-
1. Distance:
Can be performed at various distances.
-
2. Voice level:
Loud voice, often used to assess severe hearing loss.
-
3. Interpretation:
If the patient can only respond to loud voices, they may have significant hearing loss.
Clinical Application
The CVT using whispered, conversation, and loud voices can provide a rough estimate of a patient's hearing threshold and help identify potential hearing loss. However, formal audiologic evaluation is necessary for accurate diagnosis and management.
Practical Approach To CVT Using Arm-Length
Using arm length to estimate distance for the Clinical Voice Test (CVT) can be a practical approach. Here’s how:
Arm Length Estimation
-
1. Measure or estimate arm length:
Assume an arm length of approximately 60-70 cm (24-28 inches) from shoulder to wrist.
-
2. Use arm length as a guide:
Use your arm length to estimate the distance between yourself and the patient.
Performing the CVT
-
1. Stand at a distance:
Stand at a distance of 2-3 arm lengths away from the patient.
-
2. Whisper or speak:
Whisper or speak at a normal voice level, and ask the patient to repeat what they hear.
-
3. Assess response:
Assess the patient's response and adjust the distance or voice level as needed.
To assess the ears separately using the Clinical Voice Test (CVT), you can use the following method:
Assessing Each Ear Separately
-
1. Occlude one ear:
Use a finger to gently occlude one of the patient's ears.
-
2. Perform the CVT:
Perform the CVT on the un-occluded ear, whispering words or numbers at a standardized distance.
-
3. Assess response:
Assess the patient's response and note their ability to hear.
-
4. Repeat on the other ear:
Repeat the process on the other ear, occluding the previously tested ear.
Rationale
By occluding one ear and testing the other, you can assess the hearing in each ear separately. This can help identify any differences in hearing between the two ears.
Limitations
While using arm length can be a useful estimation tool, it's essential to remember that arm length can vary between individuals. For more accurate results, consider using a measuring tape or a standardized distance.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Nuggets of ORL-OTOLOGY
-
Nuggets of ORL-RHINOLOGY
-
Nuggets of Otorhinolaryngology-Basic sciences
-
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Soft Palate
-
Ethmoidal Arteries Ligation for Epistaxis
-
Submucous Cleft Palate (SMCP)
-
Approach to Ligation of the External Carotid Artery
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body in the nasal cavity.
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
-
Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation (ESPAL) for Epistaxis
-
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
Categories
RELATED POSTS
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.

