Asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss (ASNHL)
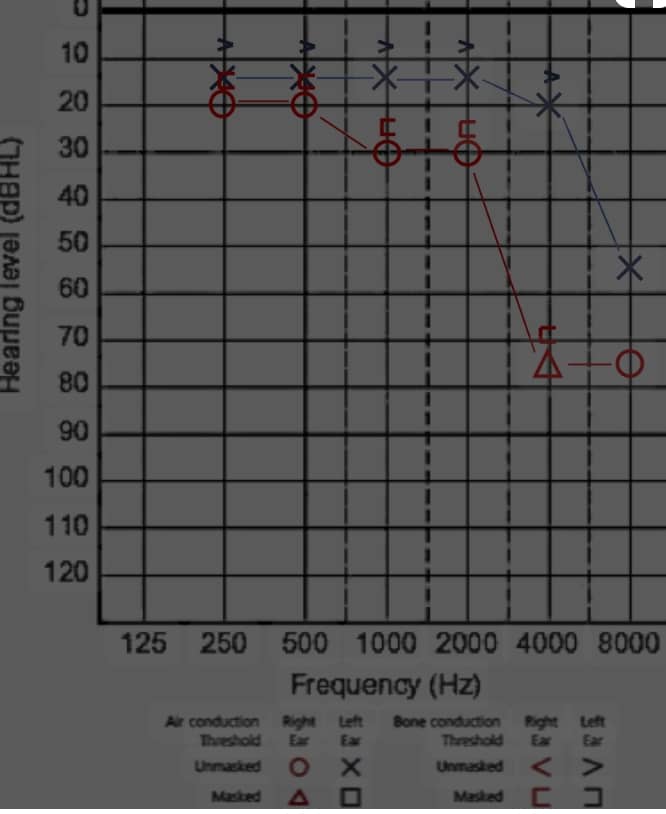
Asymmetric sensorineural hearing loss (ASNHL) refers to a condition where there is a significant difference in hearing thresholds between the two ears, with one ear having a greater degree of sensorineural hearing loss than the other.
Epidemiology
1. Prevalence: ASNHL affects approximately 1-5% of the general population.
2. Age: ASNHL can occur at any age, but it's more common in adults.
3. Sex: Both males and females are equally affected.
Pathophysiology
The exact cause of ASNHL is often unknown, but possible mechanisms include:
1. Viral infections: Viral infections, such as herpes simplex or influenza, may trigger ASNHL.
2. Vascular disorders: Reduced blood flow to the inner ear or cochlea may contribute to ASNHL.
3. Immune system disorders: Autoimmune diseases, such as rheumatoid arthritis or lupus, may increase the risk of ASNHL.
4. Trauma: Head trauma or barotrauma (e.g., scuba diving) may cause ASNHL.
5. Neoplasms: Tumors, such as acoustic neuromas, may cause ASNHL.
6. Sickle cell: haemoglobinopathy with vaso-occlusive crisis etc
Symptoms and signs
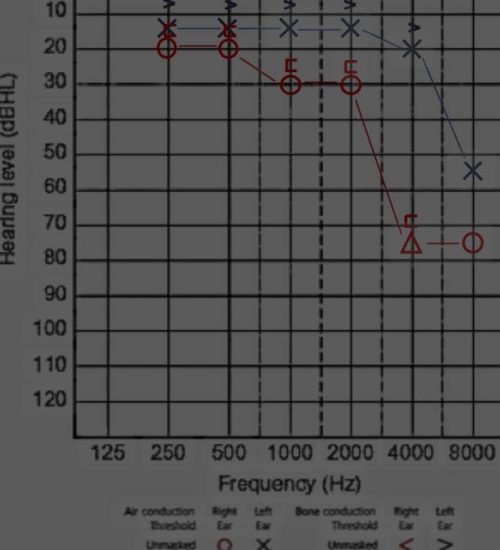
1. Asymmetric hearing loss: Hearing loss in one ear is significantly greater than in the other ear.
2. Tinnitus: Ringing, buzzing, or other sounds in the affected ear.
3. Vertigo: Dizziness or balance problems.
4. Ear fullness: Feeling of fullness or pressure in the affected ear.
Investigations
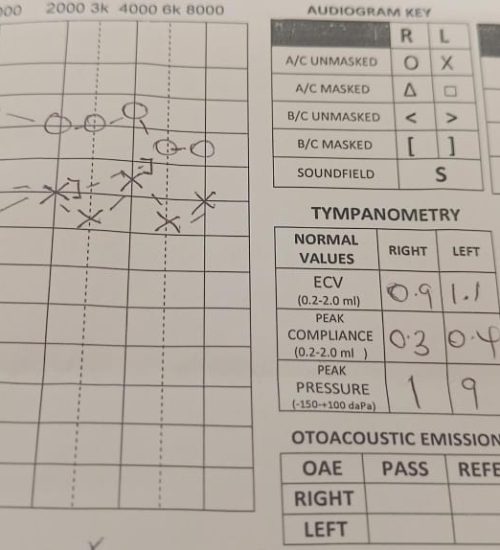
1. Pure-tone audiometry: Measures hearing thresholds to assess the extent of hearing loss.
2. Speech audiometry: Evaluates speech recognition and comprehension.
3. Otoacoustic emissions (OAEs): Measures the inner ear's response to sound.
4. Imaging studies: CT or MRI scans to rule out other conditions, such as acoustic neuromas or stroke.
5. Blood tests: To identify potential underlying causes, such as autoimmune disorders or infections, such as FbC, ESR, sickling/ Haemoglobin electrophoresis, lipid profile etc
Management
1. Corticosteroids: Oral or intratympanic (through the eardrum) corticosteroids to reduce inflammation.
2. Antiviral medications: In cases where a viral infection is suspected.
3. Hyperbaric oxygen therapy: To improve blood flow and oxygenation to the inner ear.
4. Cochlear implants: In cases where hearing loss is severe and permanent.
5. Rehabilitation: Auditory rehabilitation, including hearing aids, speech therapy, and counseling.
Prognosis
1. Spontaneous recovery: Approximately 50% of patients experience spontaneous recovery within 2-3 weeks.
2. Treatment outcomes: Prompt treatment can improve outcomes, but the effectiveness of treatment varies depending on the underlying cause and severity of hearing loss.
3. Monitoring: Regular monitoring is essential to detect any changes in hearing thresholds or to identify potential complications.
Remember, it’s essential to seek medical attention if you experience any symptoms of ASNHL, as prompt treatment can improve outcomes.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Nuggets of ORL-OTOLOGY
-
Nuggets of ORL-RHINOLOGY
-
Nuggets of Otorhinolaryngology-Basic sciences
-
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Soft Palate
-
Ethmoidal Arteries Ligation for Epistaxis
-
Submucous Cleft Palate (SMCP)
-
Approach to Ligation of the External Carotid Artery
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body in the nasal cavity.
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
-
Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation (ESPAL) for Epistaxis
-
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
Categories
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.

