Allergic rhinitis (AR)
Definition:
Allergic rhinitis (AR), also known as hay fever, is a chronic inflammatory disorder of the nasal mucosa, characterized by an overreaction of the immune system to airborne allergens, such as pollen, dust mites, or pet dander.
Epidemiology
1. Prevalence: AR affects approximately 8-10% of the global population.
2. Age: AR can occur at any age, but it typically peaks during childhood and adolescence.
3. Sex: Both males and females are equally affected.
Pathophysiology
1. Allergen exposure: Airborne allergens enter the nasal cavity and are recognized by immune cells.
2. Immunoglobulin E (IgE) production: IgE antibodies are produced in response to the allergen.
3. Mast cell activation: IgE binds to mast cells, triggering the release of histamine and other chemical mediators.
4. Inflammation and symptoms: Histamine and other mediators cause blood vessels to dilate, leading to increased mucus production, congestion, and other symptoms.
Types of Allergic Rhinitis
1. Seasonal allergic rhinitis (SAR): Caused by seasonal allergens like pollen.
2. Perennial allergic rhinitis (PAR): Caused by year-round allergens like dust mites, pet dander, or mold.
3. Occupational allergic rhinitis: Caused by workplace allergens.
Symptoms and signs
1. Nasal congestion: Stuffy or blocked nose.
2. Rhinorrhea: Runny nose, with thin, clear discharge.
3. Sneezing: Repeated frequent sneezing, usually in bursts when exposed to offending aero-allergens
4. Headache: Frequent headaches due to sinus pressure.
5. Loss of smell: Reduced sense of smell.
6. Eye symptoms: Itchy, watery, or red eyes.
7. Fatigue: Feeling tired or exhausted.
8. Itchy nose: Nasal itching; irritation and discomfort.
9. Otalgia: Earache due to sinus pressure.
Causes
1. Allergens: Pollens, dust mites, per dander, mold, cockroach allergens.
2. Genetics: Family history of atopy, allergies or asthma increases the risk.
3. Environmental factors: Exposure to allergens, air pollution, tobacco, dust.
4. Others: Exposure to strong scented perfume, soap, body and hair lotions, paint, spices etc.
Investigations
1. Medical history: Detailed history of symptoms and allergies.
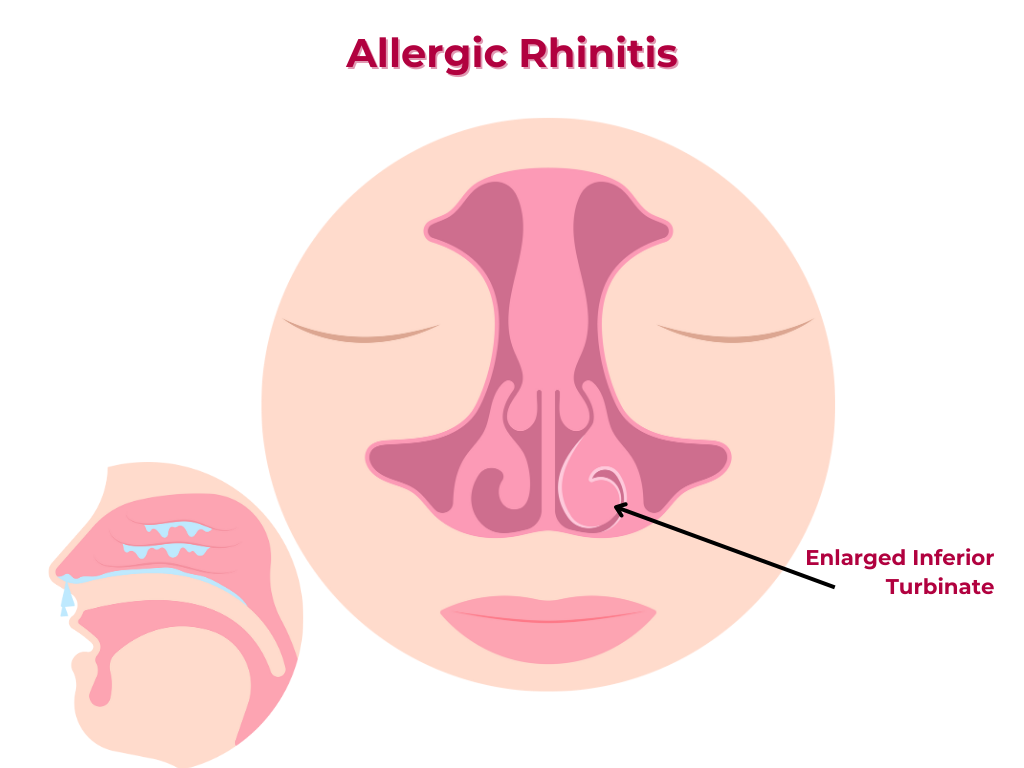
2. Physical examination: Nasal examination and assessment of eye symptoms. Nasal examination may reveal pale hypertrophic turbinates, thin watery discharge if active etc.
3. Allergy testing: Skin prick test (SPT) or blood tests (e.g., radioallergosorbent test (RAST)).
4. Nasal endoscopy: Examination of the nasal cavity using a flexible nasolaryngoscope or a rigid nasendoscope with a camera can be helpful in making the diagnosis.
Complications of Allergic Rhinitis
1. Sinusitis: Inflammation of the sinuses.
2. Sleep disturbances: Disrupted sleep patterns due to nasal congestion and discomfort
3. Impaired cognitive function: Reduced concentration and memory.
4. Asthma: Increased risk of developing asthma.
5. Otitis media: Increased risk of ear infections due to eustachian oedema and dysfunction.
Management of Allergic Rhinitis
1. Avoidance of allergens: Identify and avoid triggers.
2. Pharmacological treatment: Antihistamines, nasal corticosteroids, and decongestants.
3. Immunotherapy: Allergy shots or sublingual immunotherapy to desensitize against specific allergens.
4. Surgical treatment: Turbinate reduction or septoplasty in cases of nasal obstruction.
5. Nasal filters: Adhesive filters placed inside the nostrils to filter out allergens.
Prevention
1. Avoid strong fragrances: Avoid exposure to strong perfumes, cleaning products, and pesticides.
2. Use HEPA filters: High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters can reduce allergen exposure.
3. Keep a clean environment: Clean regularly clean surfaces, carpets, and upholstered furniture.
4. Consider immunotherapy: If symptoms persist consider immunotherapy to desensitize against specific allergens.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Nuggets of ORL-RHINOLOGY
-
Nuggets of Otorhinolaryngology-Basic sciences
-
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Soft Palate
-
Ethmoidal Arteries Ligation for Epistaxis
-
Submucous Cleft Palate (SMCP)
-
Approach to Ligation of the External Carotid Artery
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body in the nasal cavity.
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
-
Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation (ESPAL) for Epistaxis
-
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
Categories
RELATED POSTS
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.

