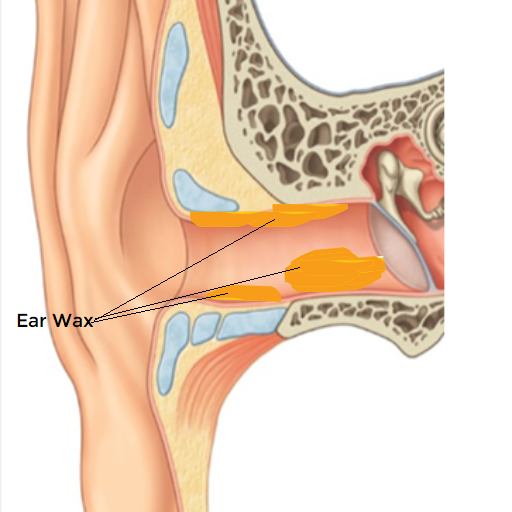
Earwax, also known as cerumen, is a natural substance produced by the glands in the ear canal. It plays a crucial role in maintaining ear health, but excessive earwax can cause problems.
The Good of Earwax
-
Protection
Earwax acts as a barrier against dust, dirt, bacteria, and other foreign particles that could harm the ear canal or eardrum.
-
Lubrication
Earwax helps to lubricate the ear canal, preventing dryness and itchiness.
-
Antimicrobial properties
Earwax contains antimicrobial agents that help to prevent infections in the ear canal.
-
Cleaning
Earwax helps to clean the ear canal by trapping dirt and debris and preventing it from reaching the eardrum.
The Bad of Earwax
-
Blockages
Excessive earwax can build up and block the ear canal, leading to hearing loss, ear fullness, or discomfort.
-
Infections
If earwax is pushed too far into the ear canal, it can cause infections, such as otitis externa.
-
Discomfort:
Excessive earwax can cause discomfort, itchiness, or pain in the ear canal.
-
Impact on hearing aids:
Excessive earwax can interfere with the proper functioning of hearing aids.
Maintaining Healthy Earwax
Avoid using cotton swabs: Refrain from using cotton swabs (Q-tips) to remove earwax, as this can push the wax further into the ear canal.
Use ear drops: Use ear drops to help dissolve excess earwax.
Dry your ears: Dry your ears thoroughly after showering or bathing.
Consult a doctor: If you experience discomfort, hearing loss, or other ear problems, consult a doctor or an ear, nose, and throat (ENT) specialist.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
Categories
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.