Overview
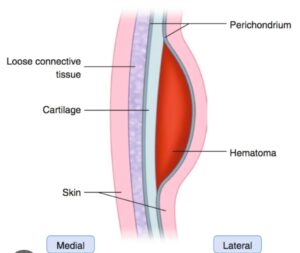
Hematoma auris, or auricular hematoma, is a collection of blood in the space between the cartilage of the ear and the perichondrium, the layer of tissue that surrounds the cartilage. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent complications.
This is often resulting from trauma.
Anatomical Layers of the Auricle
From skin to cartilage, the layers are:
1. Skin: The outermost layer.
2. Subcutaneous tissue: Connective tissue beneath the skin.
3. Perichondrium: A layer of fibrous connective tissue surrounding the cartilage.
4. Cartilage: The flexible, yet strong, connective tissue that gives the ear its shape.
5. Blood Supply of the Auricle: The auricle, or pinna, receives its blood supply from the external carotid artery through two main branches:
-
1. Posterior auricular artery
Supplies the posterior aspect of the auricle.
-
2. Anterior auricular branches of the superficial temporal artery
Supply the anterior aspect of the auricle.
Blood Supply to the Perichondrium and Cartilage
The perichondrium, a layer of fibrous connective tissue surrounding the cartilage, receives its blood supply from the same arteries that supply the auricle. The blood vessels branch out and form a network of capillaries that supply the perichondrium.
The cartilage itself is avascular, meaning it does not have a direct blood supply. Instead, it relies on diffusion of oxygen and nutrients from the surrounding perichondrium. The perichondrium plays a crucial role in providing the necessary nutrients and oxygen to the cartilage.
Importance of Blood Supply
Understanding the blood supply to the auricle, perichondrium, and cartilage is essential in various clinical contexts, such as:
-
1. Trauma
Damage to the blood supply can lead to complications, such as hematoma formation or cartilage necrosis.
-
2. Surgery
Knowledge of the blood supply is crucial for surgical procedures, such as otoplasty or reconstruction of the auricle.
-
3. Infection
Understanding the blood supply can help in managing infections, such as perichondritis, which can compromise the blood supply to the cartilage.
Epidemiology
Auricular hematomas can occur in anyone, but they are more common in individuals who participate in contact sports or activities that increase the risk of ear trauma.
Pathophysiology
The hematoma forms when blood accumulates between the cartilage and the perichondrium, often due to a shearing force that disrupts the blood vessels.
Aetiological Factors
-
1. Trauma
Blunt trauma to the ear, such as from a punch or a fall.
-
2. Contact sports
Participation in sports like wrestling, rugby, or boxing increases the risk.
Symptoms & Signs
Symptoms
1. Pain: The ear may be painful, especially when touched or moved.
2. Swelling: The ear may become swollen and tender.
3. Deformity: The ear may appear deformed or misshapen.
Signs
1. Ecchymosis: Bruising around the ear.
2. Fluctuance: A fluid collection may be palpable.
3. Tenderness: The ear is tender to the touch.
Complications
-
1. Auricular perichondritis
Infection of the perichondrium.
-
2. Auricular abscess
A collection of pus in the ear.
-
3. Cauliflower ear
A deformity of the ear that can occur if the hematoma is not properly treated.
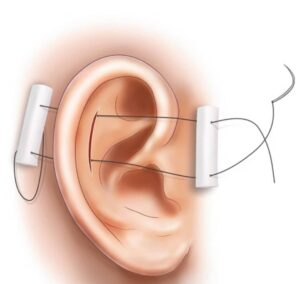
Step-by-Step Procedure of Incision and Drainage
-
1. Preparation
The area is cleaned and prepared for the procedure.
-
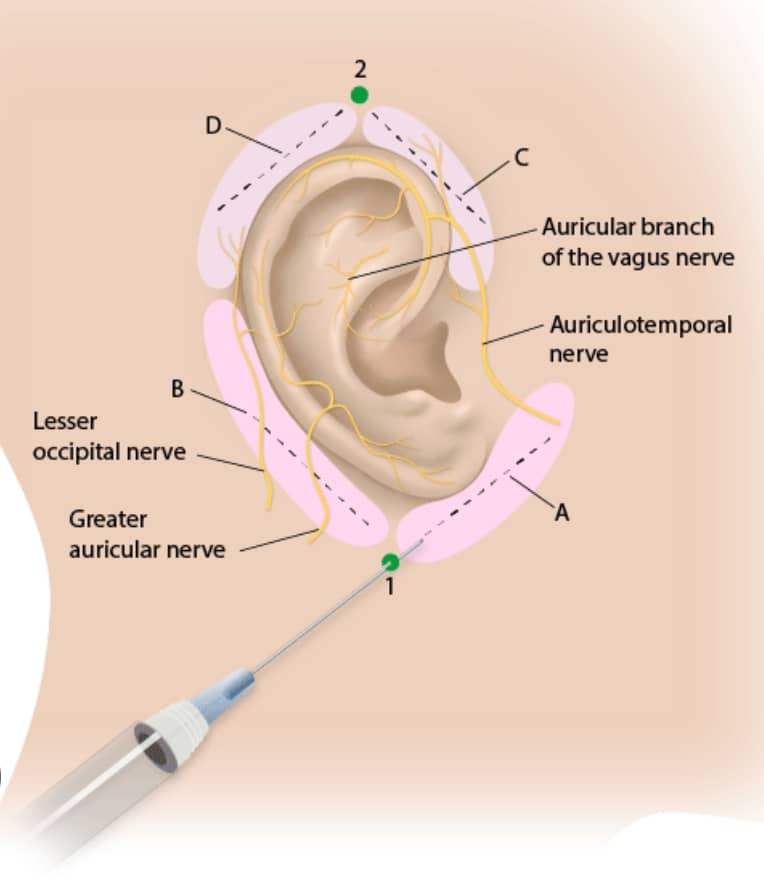
2. Anesthesia
Local anesthesia is typically used to numb the area.
-
3. Incision
A small incision is made to access the hematoma.
-
4. Drainage
The blood is drained from the hematoma.
-
5. Irrigation
The area is irrigated with saline solution.
-
6. Packing
The area may be packed with gauze or a bolster dressing to prevent reaccumulating of blood.
Postoperative Management
-
1. Pain management
Pain relief medication may be prescribed.
-
2. Antibiotics
May be prescribed to prevent infection.
-
3. Follow-up
Regular follow-up appointments are necessary to monitor healing and remove any packing.
Note on Auricular Perichondritis, Auricular Abscess, Cauliflower Ear, and Their Managements
-
1. Auricular perichondritis
Treated with antibiotics and may require hospitalization in severe cases.
-
2. Auricular abscess
May require incision and drainage, as well as antibiotics.
-
3. Cauliflower ear
Prevention is key, and prompt treatment of auricular hematomas can help prevent this complication. Treatment may involve draining the hematoma and applying a compressive dressing.
Ear Prosthesis
In cases of severe ear trauma or deformity, an ear prosthesis may be considered as a reconstructive option.
Incision and drainage of hematoma auris, is a procedure that requires careful consideration and proper technique to prevent complications. Prompt treatment is essential to prevent long-term damage and deformity
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Nuggets of ORL-OTOLOGY
-
Nuggets of ORL-RHINOLOGY
-
Nuggets of Otorhinolaryngology-Basic sciences
-
Anatomy of the Muscles of the Soft Palate
-
Ethmoidal Arteries Ligation for Epistaxis
-
Submucous Cleft Palate (SMCP)
-
Approach to Ligation of the External Carotid Artery
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body in the nasal cavity.
-
Approach to Managing a 3-Year-Old Boy with a Foreign Body impacted in the ear canal.
-
Endoscopic Sphenopalatine Artery Ligation (ESPAL) for Epistaxis
-
Surgical Management of Epistaxis
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
-
Tracheostomy
-
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
-
Acute Epiglottitis And Approach To Management
-
Synoptic Overview Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
Prioritizing Support For People With Disabilities Over Unhealthy Competitions That Marginalise The Downtrodden
-
Otitic Barotrauma
-
Titbits of Informed Consent Process for a Medical or Surgical Procedure
-
Comprehensive Overview of Mpox (Monkeypox)
-
Overview Of Corrosive Ingestion - Acid & Alkalis, and Management Approach
-
Ethical Conundrum
-
Comprehensive Overview of Laryngeal Papillomatosis and HPV Virus
-
All You Need To *Know About Gardasil*
-
Preauricular Sinus
-
Laryngomalacia - comprehensive overview
-
Flexible Laryngoscopy features of Laryngomalacia
Categories
RELATED POSTS
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.