Overview of Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM)
Overview
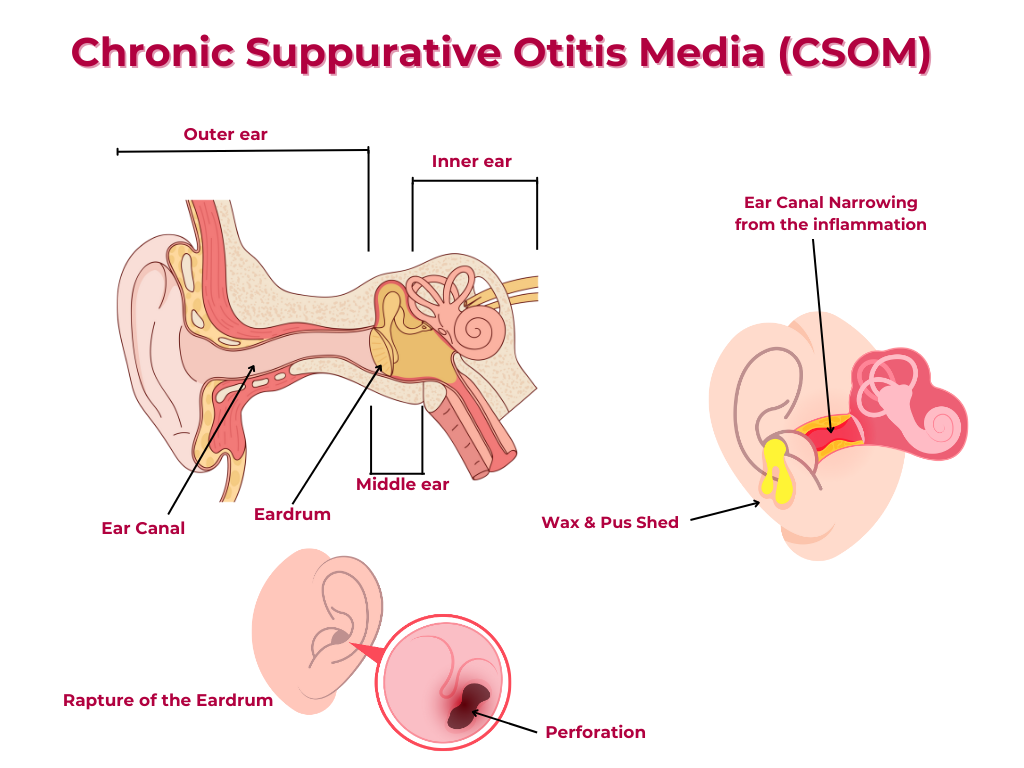
Chronic Suppurative Otitis Media (CSOM) is a chronic infection of the middle ear cleft, characterized by a persistent or recurrent discharge from the ear through a perforation in the tympanic membrane. The middle ear cleft consists of the middle ear or tympanic cavity, Eustachian tube, additus ad antrum. and the mastoid cavity and air-cell systems.
Epidemiology
1. Prevalence: CSOM affects approximately 2-5% of the global population.
2. Age: CSOM can occur at any age, but it's more common in children and young adults.
3. Socioeconomic factors: CSOM is more prevalent in low-income communities with poor sanitation and limited access to healthcare.
Pathological Types
The different types include the following:
Tubotympanic Type
1. Characterized by: Infection of the middle ear cleft via the Eustachian tube.
2. Perforation: Central perforation of the tympanic membrane.
Cholesteatoma Type
1. Characterized by: Presence of a cholesteatoma, a cyst-like structure filled with keratin debris.
2. Perforation: Marginal or attic perforation of the tympanic membrane.
Symptoms and Signs (Tubotympanic Type)
Active Stage
1. Discharge: Purulent discharge from the ear at the time of examination. Middle ear mucosa inflamed and oedematous.
2. Hearing loss: Conductive hearing loss.
3. Pain: Ear pain or discomfort.
Quiescent Stage
1. Discharge: In the recent past, discharge present but there is no discharge now. Middle ear mucosa may be oedematous.
2. Hearing loss: Persistent conductive hearing loss.
Inactive Stage
1. Discharge: No discharge for 3-6 months. Dry ear. Middle ear mucosa not inflamed.
2. Hearing loss: Persistent conductive hearing loss.
Healed Stage
1. Tympanic membrane: Intact tympanic membrane.
2. Hearing: Normal hearing
3. Infection: Permanently controlled middle ear infection.
Cholesteatoma
Theories of Formation
-
1. Epithelial Migration ( Immigration ) Theory
Skin cells migrate into the middle ear through a perforation.
-
2. Squamous Metaplasia Theory
Middle ear mucosa undergoes metaplastic changes to form into keratinizing epithelium or skin cells, which then forms a cholesteatoma.
-
3. Retraction pocket ( Invagination theory )
This theory suggests that cholesteatoma develops when a retraction pocket, formed due to eustachian tube dysfunction and negative pressure in the middle ear, traps squamous epithelium and keratin debris.
-
4. Congenital
This theory holds that small Inflammatory injury of the tympanic membrane near the neck of the malleus causes invagination of the epithelium that progresses to form a congenital cholesteatoma. This event may occur in utero during childhood development. The retracted tympanic membrane is adherent to the malleus or incus.
Complications of CSOM
1. Mastoiditis: Infection of the mastoid bone.
2. Petrous apicitis: Infection of the petrous apex.
3. Cranial nerve involvement: Infection can affect nearby cranial nerves.
4. Intracranial complications: Meningitis, brain abscess, or lateral sinus thrombosis.
4. Hearing loss: Permanent conductive, sensorineural or mixed hearing loss.
5. Facial: nerve paralysis
6. Labyrinthitis
Management of CSOM
1. Aural toilet: Cleaning of the ear canal and removal of debris.
2. Antibiotics: Topical or systemic antibiotics to control infection.
3. Tympanoplasty: Surgical repair of the tympanic membrane and middle ear.
4. Mastoidectomy: Surgical removal of infected mastoid bone.
5. Hearing rehabilitation: Hearing aids or cochlear implants to manage hearing loss.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
-
Tracheostomy
-
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
-
Acute Epiglottitis And Approach To Management
-
Synoptic Overview Of Nasopharyngeal Carcinoma
-
Prioritizing Support For People With Disabilities Over Unhealthy Competitions That Marginalise The Downtrodden
-
Otitic Barotrauma
-
Titbits of Informed Consent Process for a Medical or Surgical Procedure
-
Comprehensive Overview of Mpox (Monkeypox)
-
Overview Of Corrosive Ingestion - Acid & Alkalis, and Management Approach
-
Ethical Conundrum
-
Comprehensive Overview of Laryngeal Papillomatosis and HPV Virus
Categories
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.

