What is rhinosinusitis?
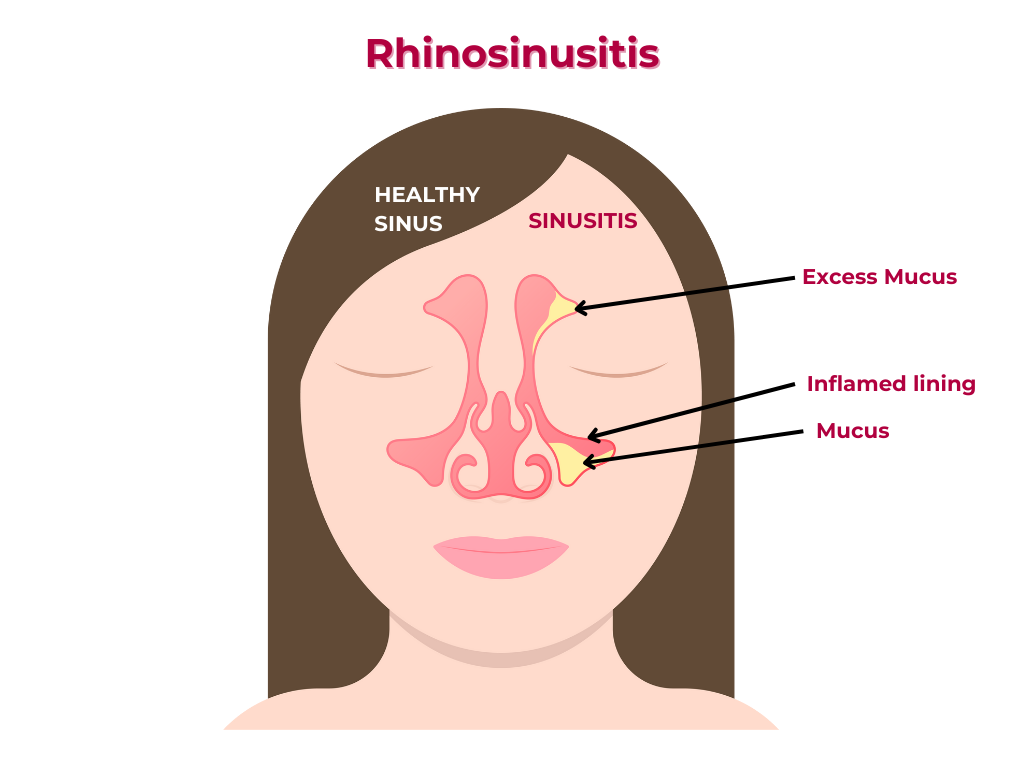
Definition:
Rhinosinusitis is inflammation of the nasal passages (rhinitis) and sinuses (sinusitis), often caused by infection, allergies, anatomical anomalies etc.
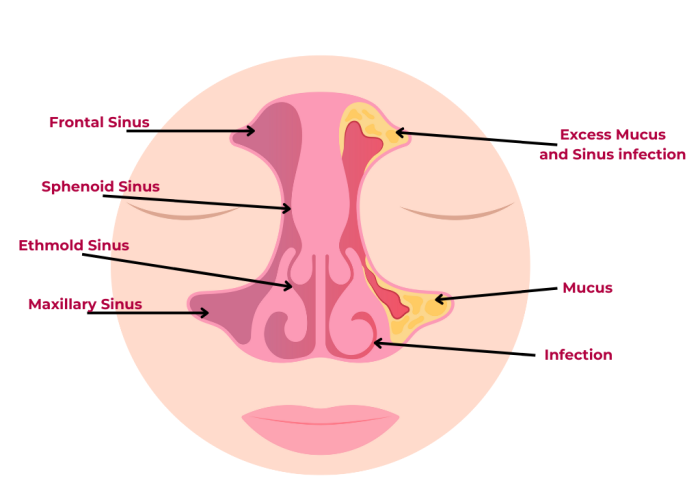
Epidemiology
1. Prevalence: Rhinosinusitis affects approximately 10-15% of the global population.
2. Age: Rhinosinusitis can occur at any age, but it's more common in adults.
3. Sex: Women are more likely to develop rhinosinusitis than men.
Pathophysiology
1. Infection: Viral, bacterial or fungal infections can cause rhinosinusitis.
2. Allergies: Allergies to pollen, dust, or other substances can trigger rhinosinusitis.
3. Anatomical abnormalities: Deviated septum, nasal polyps, or other anatomical issues can contribute to rhinosinusitis.
4. Miscellaneous factors: Factors such as nasal packing for epistaxis, passage of nasogastric tube for therapeutic purposes.
Symptoms and signs
1. Nasal congestion: Stuffy or blocked nose.
2. Yellow or green nasal discharge or post nasal drip: Thick, discolored mucus.
3. Facial pain: Pain or pressure in the cheeks, forehead, or eyes.
4. Headache: Frequent or severe headaches.
5. Loss of smell: Reduced or complete loss of sense of smell.
6. Cough: Persistent or severe cough.
7. Fatigue: Feeling tired or exhausted.
8. Halitosis: Having a bad breath.
Investigations
1. Physical examination: Nasal endoscopy or rhinoscopy.
2. Imaging tests: Computed tomography (CT) or magnetic resonance imaging (MRI) scans. CT is the gold standard tool for investigations.
3. Allergy testing*: Skin prick test or blood tests.
4. Nasal swabs*: To identify bacterial, fungal or viral infections
Management of rhinosinusitis.
Medical Management
1. Antibiotics: For bacterial infections.
2. Decongestants: To relieve nasal congestion.
3. Steroid nasal sprays: To reduce inflammation.
4. Antihistaminces: For allergies.
5. Analgesics: For headache, facial pains
Surgical Management
1. Endoscopic sinus surgery: To remove blockages or growths.
2. Septoplasty: To correct deviated septum.
3. Turbinate reduction: To reduce nasal congestion.
Lifestyle Changes
1. Nasal saline irrigation: To clear nasal passages.
2. Humidifiers: To add moisture to the air.
3. Avoid allergens: Identify and avoid triggers.
4. Quit smoking: Smoking can exacerbate rhinosinusitis.
Complications
1. Orbital complications: The most common complications
2. Chronic sinusitis: Persistent or recurring sinus infections.
3. Nasal polyps: Growths in the nasal passages.
4. Asthma: Rhinosinusitis can trigger or worsen asthma.
5. Meningitis: Rarely, rhinosinusitis can spread to the brain and cause meningitis.
Share Post On:
Recent Posts
-
Technique of Incision and Drainage of Septal Hematoma/Septal Abscess
-
Upper Aerodigestive Tract Foreign Body Impaction
-
Incision and Drainage of Hematoma Auris
-
Rigid Bronchoscopy for Retrieval of Foreign Bodies in Children
-
Foreign Body Impaction in the Larynx, Trachea, and Bronchi
-
Leadership Position is a Tool, not a Trophy
-
Carcinoma of the Oropharynx
-
Peritonsillar Abscess
-
Ethics of Doctor-Patient Relationship
-
Doctor-Patient Relationship Case Scenarios
-
Asymmetrical Tonsils and Approach to Evaluation and Management
-
Nasal Polyposis
-
Rigid Oesophagoscopy and Complication
-
Anatomy of Oesophagus
-
Stridor, Snoring, Stertor And Wheezing: How They Compare
-
Temporomandibular Joint (TMJ)
-
Otoacoustic Emissions
-
Tympanometry
-
Functional Endoscopic Sinus Surgery (FESS)
-
Tracheostomy
-
Clinical Voice Test (CVT) for Hearing Loss
Categories
Get in Touch
Read doctor-produced health and medical information written for you to make informed decisions about your health concerns.

